Phosphorylation of SOX9 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A enhances SOX9's ability to transactivate a Col2a1 chondrocyte-specific enhancer
- PMID: 10805756
- PMCID: PMC85784
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.11.4149-4158.2000
Phosphorylation of SOX9 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A enhances SOX9's ability to transactivate a Col2a1 chondrocyte-specific enhancer
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol 2000 Oct;20(20):7838
Abstract
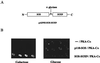
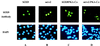
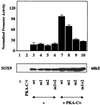
Sox9 is a high-mobility-group domain-containing transcription factor required for chondrocyte differentiation and cartilage formation. We used a yeast two-hybrid method based on Son of Sevenless (SOS) recruitment to screen a chondrocyte cDNA library and found that the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase A (PKA-Calpha) interacted specifically with SOX9. Next we found that two consensus PKA phosphorylation sites within SOX9 could be phosphorylated by PKA in vitro and that SOX9 could be phosphorylated by PKA-Calpha in vivo. In COS-7 cells cotransfected with PKA-Calpha and SOX9 expression plasmids, PKA enhanced the phosphorylation of wild-type SOX9 but did not affect phosphorylation of a SOX9 protein in which the two PKA phosphorylation sites (S(64) and S(211)) were mutated. Using a phosphospecific antibody that specifically recognized SOX9 phosphorylated at serine 211, one of the two PKA phosphorylation sites, we demonstrated that addition of cAMP to chondrocytes strongly increased the phosphorylation of endogenous Sox9. In addition, immunohistochemistry of mouse embryo hind legs showed that Sox9 phosphorylated at serine 211 was principally localized in the prehypertrophic zone of the growth plate, corresponding to the major site of expression of the parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) receptor. Since cAMP has previously been shown to effectively increase the mRNA levels of Col2a1 and other specific markers of chondrocyte differentiation in culture, we then asked whether PKA phosphorylation could modulate the activity of SOX9. Addition of 8-bromo-cAMP to chondrocytes in culture increased the activity of a transiently transfected SOX9-dependent 48-bp Col2a1 chondrocyte-specific enhancer; similarly, cotransfection of PKA-Calpha increased the activity of this enhancer. Mutations of the two PKA phosphorylation consensus sites of SOX9 markedly decreased the PKA-Calpha activation of this enhancer by SOX9. PKA phosphorylation and the mutations in the consensus PKA phosphorylation sites of SOX9 did not alter its nuclear localization. In vitro phosphorylation of SOX9 by PKA resulted in more efficient DNA binding. We conclude that SOX9 is a target of cAMP signaling and that phosphorylation of SOX9 by PKA enhances its transcriptional and DNA-binding activity. Because PTHrP signaling is mediated by cAMP, our results support the hypothesis that Sox9 is a target of PTHrP signaling in the growth plate and that the increased activity of Sox9 might mediate the effect of PTHrP in maintaining the cells as nonhypertrophic chondrocytes.
Figures



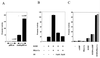


Similar articles
-
The chondrogenic transcription factor Sox9 is a target of signaling by the parathyroid hormone-related peptide in the growth plate of endochondral bones.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jan 2;98(1):160-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.1.160. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11120880 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional mechanisms of chondrocyte differentiation.Matrix Biol. 2000 Sep;19(5):389-94. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(00)00094-9. Matrix Biol. 2000. PMID: 10980415 Review.
-
Three high mobility group-like sequences within a 48-base pair enhancer of the Col2a1 gene are required for cartilage-specific expression in vivo.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 12;273(24):14989-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.24.14989. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9614106
-
SOX9 is a potent activator of the chondrocyte-specific enhancer of the pro alpha1(II) collagen gene.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2336-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2336. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121483 Free PMC article.
-
Toward understanding SOX9 function in chondrocyte differentiation.Matrix Biol. 1998 Mar;16(9):529-40. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(98)90065-8. Matrix Biol. 1998. PMID: 9569122 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies to minimize hypertrophy in cartilage engineering and regeneration.Genes Dis. 2015 Mar 1;2(1):76-95. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.12.003. Genes Dis. 2015. PMID: 26000333 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9-regulated cell plasticity in colorectal metastasis is attenuated by rapamycin.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 30;6:32350. doi: 10.1038/srep32350. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27571710 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factors SF-1 and SOX8 cooperate to upregulate Cx43 expression in mouse TM4 sertoli cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020 Oct 10;24:100828. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100828. eCollection 2020 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020. PMID: 33088929 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase-dependent activation of SOX9 in chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Jan;62(1):191-200. doi: 10.1002/art.25051. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20039424 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning of mesenchymal stromal cells with low-intensity ultrasound: influence on chondrogenesis and directed SOX9 signaling pathways.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jan 3;11(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1532-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 31900222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell D M, Leung K K H, Whearley S C, Ng L J, Zhou S, Ling K W, Sham M H, Koopman P, Tam P P L, Cheah K S E. Sox9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet. 1997;16:174–178. - PubMed
-
- Bi W, Deng J, Zhang Z, Behringer R R, de Crombrugghe B. Sox9 is required for cartilage formation. Nat Genet. 1999;22:85–89. - PubMed
-
- Boulikas T. Phosphorylation of transcription factors and control of the cell cycle. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expression. 1995;5:1–77. - PubMed
-
- Bridgewater L C, Lefebvre V, de Crombrugghe B. Chondrocyte-specific enhancer elements in the Col11a2 gene resemble the Col2a1 tissue-specific enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14998–15006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
