15-deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits multiple steps in the NF-kappa B signaling pathway
- PMID: 10781090
- PMCID: PMC18320
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.9.4844
15-deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits multiple steps in the NF-kappa B signaling pathway
Abstract
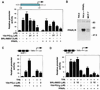
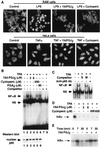
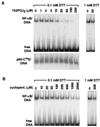
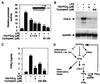
Prostaglandin J(2) (PGJ(2)) and its metabolites Delta(12)-PGJ(2) and 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-PGJ(2) (15d-PGJ(2)) are naturally occurring derivatives of prostaglandin D(2) that have been suggested to exert antiinflammatory effects in vivo. 15d-PGJ(2) is a high-affinity ligand for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and has been demonstrated to inhibit the induction of inflammatory response genes, including inducible NO synthase and tumor necrosis factor alpha, in a PPARgamma-dependent manner. We report here that 15d-PGJ(2) potently inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent transcription by two additional PPARgamma-independent mechanisms. Several lines of evidence suggest that 15d-PGJ(2) directly inhibits NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression through covalent modifications of critical cysteine residues in IkappaB kinase and the DNA-binding domains of NF-kappaB subunits. These mechanisms act in combination to inhibit transactivation of the NF-kappaB target gene cyclooxygenase 2. Direct inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by 15d-PGJ(2) may contribute to negative regulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis and inflammation, suggesting additional approaches to the development of antiinflammatory drugs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2) in activated human astrocytes, but not in human brain macrophages.J Immunol. 2002 May 1;168(9):4747-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.9.4747. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11971025
-
Inhibition of activator protein 1 activation, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 in colon carcinoma cells: evidence for a redox-sensitive peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-independent mechanism.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5162-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0849. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289320
-
The 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits the inflammatory response in primary rat astrocytes via down-regulating multiple steps in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-NF-kappaB-p300 pathway independent of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.J Immunol. 2004 Oct 15;173(8):5196-208. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.8.5196. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15470065
-
15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 as a potential endogenous regulator of redox-sensitive transcription factors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Nov 30;72(11):1516-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.030. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16987499 Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligands as bifunctional regulators of cell proliferation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Oct 15;66(8):1381-91. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00488-x. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14555212 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer cachexia--pathophysiology and management.J Gastroenterol. 2013 May;48(5):574-94. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0787-0. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23512346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Eicosanoids in Regulating Inflammation and Neutrophil Migration as an Innate Host Response to Bacterial Infections.Infect Immun. 2021 Jul 15;89(8):e0009521. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00095-21. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 34031130 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of the Cyanobacterial Macrolide Glycoside Moorenaside, an Anti-Inflammatory Analogue of Aurisides Targeting the Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway.J Nat Prod. 2024 Oct 25;87(10):2355-2365. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.4c00420. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Nat Prod. 2024. PMID: 39315953 Free PMC article.
-
Human lung fibroblasts produce proresolving peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligands in a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):L855-L867. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00272.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27612965 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 15d-PGJ₂-loaded poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanocapsules on inflammation.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(3):623-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01057.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20883476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fukushima M. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent Fatty Acids. 1992;47:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Forman B M, Tontonoz P, Chen J, Brun R P, Spiegelman B M, Evans R M. Cell. 1995;83:803–812. - PubMed
-
- Kliewer S A, Lenhard J M, Willson T M, Patel I, Morris D C, Lehmann J M. Cell. 1995;83:813–819. - PubMed
-
- Ricote M, Li A C, Willson T M, Kelly C J, Glass C K. Nature (London) 1998;391:79–82. - PubMed
-
- Jiang C, Ting A T, Seed B. Nature (London) 1998;391:82–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

