Ephrin-A5 induces collapse of growth cones by activating Rho and Rho kinase
- PMID: 10769020
- PMCID: PMC2175154
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.2.263
Ephrin-A5 induces collapse of growth cones by activating Rho and Rho kinase
Abstract
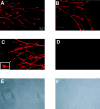
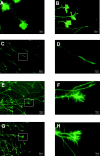
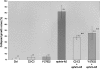
The ephrins, ligands of Eph receptor tyrosine kinases, have been shown to act as repulsive guidance molecules and to induce collapse of neuronal growth cones. For the first time, we show that the ephrin-A5 collapse is mediated by activation of the small GTPase Rho and its downstream effector Rho kinase. In ephrin-A5-treated retinal ganglion cell cultures, Rho was activated and Rac was downregulated. Pretreatment of ganglion cell axons with C3-transferase, a specific inhibitor of the Rho GTPase, or with Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of the Rho kinase, strongly reduced the collapse rate of retinal growth cones. These results suggest that activation of Rho and its downstream effector Rho kinase are important elements of the ephrin-A5 signal transduction pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cdk5/p35 and Rho-kinase mediate ephrin-A5-induced signaling in retinal ganglion cells.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003 Nov;24(3):632-45. doi: 10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00220-3. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14664814
-
The Rho/ROCK pathway mediates neurite growth-inhibitory activity associated with the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of the CNS glial scar.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003 Mar;22(3):319-30. doi: 10.1016/s1044-7431(02)00035-0. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12691734
-
A key role for Abl family kinases in EphA receptor-mediated growth cone collapse.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Sep;30(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.05.002. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15996481
-
GTPase regulation: getting aRnd Rock and Rho inhibition.Curr Biol. 2003 Sep 16;13(18):R702-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.08.042. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 13678607 Review.
-
Eph receptors and ephrins in neural development.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999 Feb;9(1):65-73. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(99)80008-7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10072375 Review.
Cited by
-
Inverse Expression Levels of EphrinA3 and EphrinA5 Contribute to Dopaminergic Differentiation of Human SH-SY5Y Cells.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Aug;59(4):483-92. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0759-y. Epub 2016 May 23. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27217159
-
EphA kinase activation regulates HGF-induced epithelial branching morphogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2003 Sep 29;162(7):1281-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304018. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14517207 Free PMC article.
-
Motor axon pathfinding.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Mar;2(3):a001735. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a001735. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20300210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EphA2 signaling following endocytosis: role of Tiam1.Traffic. 2013 Dec;14(12):1255-71. doi: 10.1111/tra.12123. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 24112471 Free PMC article.
-
RPM-1 regulates axon termination by affecting growth cone collapse and microtubule stability.Development. 2017 Dec 15;144(24):4658-4672. doi: 10.1242/dev.154187. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Development. 2017. PMID: 29084805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y., Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Arber S., Barbayannis F.A., Hanser H., Schneider C., Stanyon C.A., Bernard O., Caroni P. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature. 1998;393:805–809. - PubMed
-
- Barth H., Hofmann F., Olenik C., Just I., Aktories K. The N-terminal part of the enzyme component (C2I) of the binary Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin interacts with the binding component C2II and functions as a carrier system for a Rho ADP-ribosylating C3-like fusion toxin. Infect. Immun. 1998;66:1364–1369. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barth H., Olenik C., Sehr P., Schmidt G., Aktories K., Meyer D.K. Neosynthesis and activation of Rho by Escherichia coli necrotizing factor (CNF1) reverse cytopathic effects of ADP-ribosylated Rho. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:27407–27414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

