Response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a decrease of T cell derived tumour necrosis factor alpha, increase of interleukin 10, and predicted by the initial concentration of interleukin 4
- PMID: 10733482
- PMCID: PMC1753104
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.59.4.311
Response to methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with a decrease of T cell derived tumour necrosis factor alpha, increase of interleukin 10, and predicted by the initial concentration of interleukin 4
Abstract
Objective: This study was performed to assess whether there is any change in the T cell cytokine pattern in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with methotrexate (MTX) and whether the lymphocytic cytokine pattern correlates with disease activity.
Methods: Eight patients with RA (disease duration < six months) were studied serially before, after three, and after six to nine months of treatment with MTX for the cytokines tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), interferon gamma (IFNgamma), interleukin 4 (IL4) and interleukin 10 (IL10) by intracellular staining of T cells derived from peripheral blood. Response to treatment was assessed by the modified disease activitiy score.
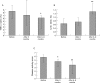
Results: The clincial response was accompanied by a significant decrease of TNFalpha positive CD4(+) T cells from a median of 8.53% (interquartile range 5.83-10.91%) before treatment to 6.17% (2.15-6.81%) after six to nine months of treatment (p=0.021). Inversely, IL10 positive T cells increased from a median of 0.65% (interquartile range 0.6-0.93%) to a median of 1. 3% (1.22%-1.58%) after six to nine months of treatment (p=0.009). No significant change in the percentage of INFgamma positive T cells and a small decrease of IL4 positive T cells during treatment were observed. The percentage of IL4 positive CD4(+) T cells before treatment correlated with disease activity after six to nine months (r= -0.7066; p=0.05).
Conclusions: During treatment of RA with MTX the percentage of TNFalpha producing T cells decreases whereas that of IL10 producing T cells increases. This may affect macrophage activation and, therefore, may represent a regulatory mechanism relevant to disease remission. Furthermore, the percentage of IL4 positive CD4(+) T cells at disease onset may be a useful prognostic marker.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of a Type 2-Polarized T Cell Phenotype With Methotrexate Nonresponse in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jul;72(7):1091-1102. doi: 10.1002/art.41223. Epub 2020 May 29. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32039570
-
Impaired Th1 cytokine production in spondyloarthropathy is restored by anti-TNFalpha.Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Aug;60(8):750-5. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.8.750. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. PMID: 11454638 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of longterm therapy with methotrexate and low dose corticosteroids on type 1 and type 2 cytokine production in CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2001 Aug;28(8):1793-9. J Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11508581 Clinical Trial.
-
Leveraging blood and tissue CD4+ T cell heterogeneity at the single cell level to identify mechanisms of disease in rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Opin Immunol. 2017 Dec;49:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2017.08.005. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28888129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of cell-mediated immunity by IL4 and IL10.Res Immunol. 1993 Oct;144(8):639-43. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2494(05)80019-7. Res Immunol. 1993. PMID: 7905657 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Update on pathogenesis and predictors of response of therapeutic strategies used in inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 28;21(44):12519-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12519. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26640330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The HLA-G Immune Checkpoint Plays a Pivotal Role in the Regulation of Immune Response in Autoimmune Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13348. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413348. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products for the Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis: Their Mechanisms of Action, Targeted Delivery, and Interplay with the Host Microbiome.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 24;19(9):2508. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092508. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 10;20(20):5023. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205023. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31658782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compromised function of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by anti-TNFalpha therapy.J Exp Med. 2004 Aug 2;200(3):277-85. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040165. Epub 2004 Jul 26. J Exp Med. 2004. PMID: 15280421 Free PMC article.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
