The genome of fowlpox virus
- PMID: 10729156
- PMCID: PMC111890
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3815-3831.2000
The genome of fowlpox virus
Abstract
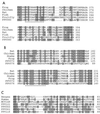
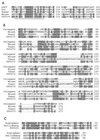
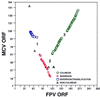
Here we present the genomic sequence, with analysis, of a pathogenic fowlpox virus (FPV). The 288-kbp FPV genome consists of a central coding region bounded by identical 9.5-kbp inverted terminal repeats and contains 260 open reading frames, of which 101 exhibit similarity to genes of known function. Comparison of the FPV genome with those of other chordopoxviruses (ChPVs) revealed 65 conserved gene homologues, encoding proteins involved in transcription and mRNA biogenesis, nucleotide metabolism, DNA replication and repair, protein processing, and virion structure. Comparison of the FPV genome with those of other ChPVs revealed extensive genome colinearity which is interrupted in FPV by a translocation and a major inversion, the presence of multiple and in some cases large gene families, and novel cellular homologues. Large numbers of cellular homologues together with 10 multigene families largely account for the marked size difference between the FPV genome (260 to 309 kbp) and other known ChPV genomes (178 to 191 kbp). Predicted proteins with putative functions involving immune evasion included eight natural killer cell receptors, four CC chemokines, three G-protein-coupled receptors, two beta nerve growth factors, transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-18-binding protein, semaphorin, and five serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins). Other potential FPV host range proteins included homologues of those involved in apoptosis (e.g., Bcl-2 protein), cell growth (e.g., epidermal growth factor domain protein), tissue tropism (e.g., ankyrin repeat-containing gene family, N1R/p28 gene family, and a T10 homologue), and avian host range (e.g., a protein present in both fowl adenovirus and Marek's disease virus). The presence of homologues of genes encoding proteins involved in steroid biogenesis (e.g., hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase), antioxidant functions (e.g., glutathione peroxidase), vesicle trafficking (e.g., two alpha-type soluble NSF attachment proteins), and other, unknown conserved cellular processes (e.g., Hal3 domain protein and GSN1/SUR4) suggests that significant modification of host cell function occurs upon viral infection. The presence of a cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase homologue in FPV suggests the presence of a photoreactivation DNA repair pathway. This diverse complement of genes with likely host range functions in FPV suggests significant viral adaptation to the avian host.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The genome of Melanoplus sanguinipes entomopoxvirus.J Virol. 1999 Jan;73(1):533-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.533-552.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9847359 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the genome sequence of FP9, an attenuated, tissue culture-adapted European strain of Fowlpox virus, with those of virulent American and European viruses.J Gen Virol. 2004 Feb;85(Pt 2):305-322. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19568-0. J Gen Virol. 2004. PMID: 14769888
-
Fowlpox virus encodes a novel DNA repair enzyme, CPD-photolyase, that restores infectivity of UV light-damaged virus.J Virol. 2001 Feb;75(4):1681-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.4.1681-1688.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160666 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA sequence of human herpesvirus-6: structure, coding content, and genome evolution.Virology. 1995 May 10;209(1):29-51. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1228. Virology. 1995. PMID: 7747482 Review.
-
Characterization of Fowlpox Virus.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1451:55-74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-57165-7_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38801571 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis prediction via inhibition of AKT signaling pathway by neogrifolin.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1154-64. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973001 Free PMC article.
-
The pp38 gene of Marek's disease virus (MDV) is necessary for cytolytic infection of B cells and maintenance of the transformed state but not for cytolytic infection of the feather follicle epithelium and horizontal spread of MDV.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4545-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4545-4549.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767457 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the archaeal thermophile Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus validates an evolutionary link among double-stranded DNA viruses from all domains of life.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7625-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00522-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840341 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pathogenic avipoxvirus infecting oriental turtle dove (Streptopelia orientalis) in China shows a high genomic and evolutionary proximity with the pigeon avipoxviruses isolated globally.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 26;11(5):e0119323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01193-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37750697 Free PMC article.
-
The complete genome sequences of poxviruses isolated from a penguin and a pigeon in South Africa and comparison to other sequenced avipoxviruses.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 12;15:463. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-463. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24919868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja S K, Murphy P M. Molecular piracy of mammalian interleukin-8 receptor type B by herpesvirus saimiri. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:20691–20694. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa Y, Akita K, Taniai M, Torigoe K, Mori T, Nishida Y, Ushio S, Nukada Y, Tanimoto T, Ikegami H, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M. Cloning and expression of interleukin-18 binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1999;445:338–342. - PubMed
-
- Alcami A, Symons J A, Collins P D, Williams T J, Smith G L. Blockade of chemokine activity by a soluble chemokine binding protein from vaccinia virus. J Immunol. 1998;160:624–633. - PubMed
-
- Aloe L, Simone M D, Properzi F. Nerve growth factor: a neurotrophin with activity on cells of the immune system. Microsc Res Tech. 1999;45:285–291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

