The carboxyl terminus of vertebrate poly(A) polymerase interacts with U2AF 65 to couple 3'-end processing and splicing
- PMID: 10691733
- PMCID: PMC316384
The carboxyl terminus of vertebrate poly(A) polymerase interacts with U2AF 65 to couple 3'-end processing and splicing
Abstract
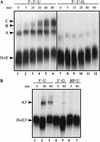
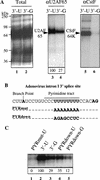
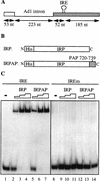
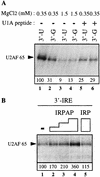
Although it has been established that the processing factors involved in pre-mRNA splicing and 3'-end formation can influence each other positively, the molecular basis of this coupling interaction was not known. Stimulation of pre-mRNA splicing by an adjacent cis-linked cleavage and polyadenylation site in HeLa cell nuclear extract is shown to occur at an early step in splicing, the binding of U2AF 65 to the pyrimidine tract of the intron 3' splice site. The carboxyl terminus of poly(A) polymerase (PAP) previously has been implicated indirectly in the coupling process. We demonstrate that a fusion protein containing the 20 carboxy-terminal amino acids of PAP, when tethered downstream of an intron, increases splicing efficiency and, like the entire 3'-end formation machinery, stimulates U2AF 65 binding to the intron. The carboxy-terminal domain of PAP makes a direct and specific interaction with residues 17-47 of U2AF 65, implicating this interaction in the coupling of splicing and 3'-end formation.
Figures


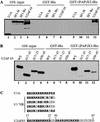
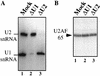
Similar articles
-
An interaction between U2AF 65 and CF I(m) links the splicing and 3' end processing machineries.EMBO J. 2006 Oct 18;25(20):4854-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601331. Epub 2006 Oct 5. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 17024186 Free PMC article.
-
The hnRNP A1 protein regulates HIV-1 tat splicing via a novel intron silencer element.EMBO J. 2001 Oct 15;20(20):5748-58. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5748. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11598017 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of new poly(A) polymerase-inhibitory proteins capable of regulating pre-mRNA polyadenylation.J Mol Biol. 2002 May 17;318(5):1189-206. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00240-1. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12083511
-
An active role for splicing in 3'-end formation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):459-70. doi: 10.1002/wrna.68. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957037 Review.
-
Non-canonical poly(A) polymerase in mammalian gametogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Apr;1779(4):230-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18294465 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of essential splicing factor ASF/SF2 blocks the temporal shift in adenovirus pre-mRNA splicing and reduces virus progeny formation.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(19):9002-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.19.9002-9009.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10982344 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of eukaryotic pre-mRNA 3' end processing regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 May;38(9):2757-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1176. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20044349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arginine methylation in subunits of mammalian pre-mRNA cleavage factor I.RNA. 2010 Aug;16(8):1646-59. doi: 10.1261/rna.2164210. Epub 2010 Jun 18. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20562214 Free PMC article.
-
Serine/arginine-rich proteins contribute to negative regulator of splicing element-stimulated polyadenylation in rous sarcoma virus.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11208-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00919-07. Epub 2007 Aug 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17670832 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-mRNA splicing during transcription in the mammalian system.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Sep-Oct;2(5):700-17. doi: 10.1002/wrna.86. Epub 2011 May 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21823230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abovich N, Rosbash M. Cross-intron bridging interactions in the yeast commitment complex are conserved in mammals. Cell. 1997;89:403–412. - PubMed
-
- Arias JA, Peterson SR, Dynan WS. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:8055–8061. - PubMed
-
- Barabino SML, Blencowe BJ, Ryder U, Sproat BS, Lamond AI. Targeted snRNP depletion reveals an additional role for mammalian U1 snRNP in spliceosome assembly. Cell. 1990;63:293–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
