Transcription factor Sp3 is essential for post-natal survival and late tooth development
- PMID: 10675334
- PMCID: PMC305603
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.655
Transcription factor Sp3 is essential for post-natal survival and late tooth development
Abstract
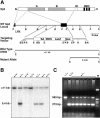
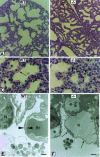
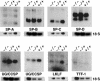
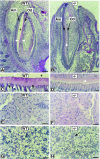
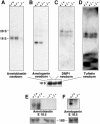
Sp3 is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor closely related to Sp1 (specificity protein 1). We have disrupted the mouse Sp3 gene by homologous recombination. Sp3-deficient embryos are growth retarded and invariably die at birth of respiratory failure. The cause for the observed breathing defect remains obscure since only minor morphological alterations were observed in the lung, and surfactant protein expression is indistinguishable from that in wild-type mice. Histological examinations of individual organs in Sp3(-/-) mice show a pronounced defect in late tooth formation. In Sp3 null mice, the dentin/enamel layer of the developing teeth is impaired due to the lack of ameloblast-specific gene products. Comparison of the Sp1 and Sp3 knockout phenotype shows that Sp1 and Sp3 have distinct functions in vivo, but also suggests a degree of functional redundancy.
Figures

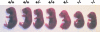
Similar articles
-
Identification of the promoter of human transcription factor Sp3 and evidence of the role of factors Sp1 and Sp3 in the expression of Sp3 protein.Gene. 2005 May 23;351:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.02.007. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15857802
-
Sp1/Sp3 compound heterozygous mice are not viable: impaired erythropoiesis and severe placental defects.Dev Dyn. 2007 Aug;236(8):2235-44. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21222. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17584888
-
LEF1 is a critical epithelial survival factor during tooth morphogenesis.Dev Biol. 2005 Feb 1;278(1):130-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.10.021. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15649466
-
Gene regulation by Sp1 and Sp3.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;82(4):460-71. doi: 10.1139/o04-045. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15284899 Review.
-
Enhanced binding of Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors mediates the hyperoxia-induced increased expression of the lung type I cell gene T1alpha.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Aug 1;89(5):887-901. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10555. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12874823
Cited by
-
Ctip2/Bcl11b controls ameloblast formation during mammalian odontogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 17;106(11):4278-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900568106. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19251658 Free PMC article.
-
Sp proteins and Runx2 mediate regulation of matrix gla protein (MGP) expression by parathyroid hormone.J Cell Biochem. 2009 May 15;107(2):284-92. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22124. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19306294 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor and specificity protein 1 (Sp1) or Sp3, but not the antibiotic Mithramycin A, stimulates human alphaherpesvirus 1 (HSV-1) replication.Antiviral Res. 2024 May;225:105870. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105870. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38556059
-
Inference of cell type-specific gene regulatory networks on cell lineages from single cell omic datasets.Nat Commun. 2023 May 27;14(1):3064. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38637-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37244909 Free PMC article.
-
Sp2 localizes to subnuclear foci associated with the nuclear matrix.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Apr;17(4):1711-22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-11-1063. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16467376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun H. and Suske, G. (1998) Combinatorial action of HNF3 and Sp family transcription factors in the activation of the rabbit uteroglobin/CC10 promoter. J. Biol. Chem., 273, 9821–9828. - PubMed
-
- Chen E., Yuan, Z.A., Collier, P.M., Greene, S.R., Abrams, W.R. and Gibson, C.W. (1998) Comparison of upstream regions of X- and Y-chromosomal amelogenin genes. Gene, 216, 131–137. - PubMed
-
- Couwenhoven R.I. and Snead, M.L. (1994) Early determination and permissive expression of amelogenin transcription during mouse mandibular first molar development. Dev. Biol., 164, 290–299. - PubMed
-
- Dennig J., Hagen, G., Beato, M. and Suske, G. (1995) Members of the Sp transcription factor family control transcription from the uteroglobin promoter. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 12737–12744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

