Optimization of the helper-dependent adenovirus system for production and potency in vivo
- PMID: 10655474
- PMCID: PMC15501
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1002
Optimization of the helper-dependent adenovirus system for production and potency in vivo
Abstract
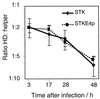
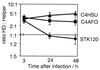
Helper-dependent (HD) adenoviral vectors devoid of all viral coding sequences provide for safe and highly efficient gene transfer with long-lasting transgene expression. High titer stocks of HD vectors can be generated by using the cre-recombinase system. However, we have encountered difficulties with this system, including rearranged HD vectors and variable efficiency of HD vector rescue. These problems represent a major hindrance, particularly with regard to large-scale production. To overcome these limitations, we have modified the system in two ways: We constructed a new helper virus with a modified packaging signal and enhanced growth characteristics. We also redesigned the vector backbones by including noncoding adenovirus sequences adjacent to the right inverted terminal repeat and by incorporated a number of different segments of noncoding DNA of human origin as "stuffer." Comparison of these vectors showed that the nature of the stuffer sequence affects replication of the HD vector. Optimization of the system resulted in a more robust and consistent production of HD vectors with low helper contamination and high in vivo potency.
Figures
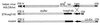
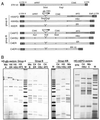
 , hvegf145-cDNA and bGH poly A; ◂,
loxP-site; arrow, CMV promoter; —, CMV intron A.
, hvegf145-cDNA and bGH poly A; ◂,
loxP-site; arrow, CMV promoter; —, CMV intron A.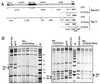

Similar articles
-
Cre levels limit packaging signal excision efficiency in the Cre/loxP helper-dependent adenoviral vector system.J Virol. 2002 May;76(9):4181-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.9.4181-4189.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11932383 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a FLP/frt system for generating helper-dependent adenoviral vectors.Mol Ther. 2001 May;3(5 Pt 1):809-15. doi: 10.1006/mthe.2001.0323. Mol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11356086
-
Generation of high-titer defective HSV-1 vectors using an IE 2 deletion mutant and quantitative study of expression in cultured cortical cells.Biotechniques. 1996 Mar;20(3):460-9. doi: 10.2144/19962003460. Biotechniques. 1996. PMID: 8679207
-
Viral vector systems for gene therapy.Cancer Gene Ther. 1994 Mar;1(1):51-64. Cancer Gene Ther. 1994. PMID: 7621239 Review. No abstract available.
-
Expanded-capacity adenoviral vectors--the helper-dependent vectors.Mol Med Today. 1999 Jan;5(1):18-24. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(98)01376-8. Mol Med Today. 1999. PMID: 10088128 Review.
Cited by
-
AAV vectors: The Rubik's cube of human gene therapy.Mol Ther. 2022 Dec 7;30(12):3515-3541. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.09.015. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36203359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Therapy Targeting LDL Cholesterol but not HDL Cholesterol Induces Regression of Advanced Atherosclerosis in a Mouse Model of Familial Hypercholesterolemia.J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2011 Sep 28;2:106. doi: 10.4172/2157-7412.1000106. J Genet Syndr Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 23106034 Free PMC article.
-
DARPin-fused T cell engager for adenovirus-mediated cancer therapy.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 May 29;32(3):200821. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200821. eCollection 2024 Sep 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39021370 Free PMC article.
-
General strategy for broadening adenovirus tropism.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(20):11094-104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.20.11094-11104.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14512557 Free PMC article.
-
Evading the immune response upon in vivo gene therapy with viral vectors.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009 Oct;11(5):493-503. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19806497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

