Modulation of major histocompatibility class II protein expression by varicella-zoster virus
- PMID: 10644363
- PMCID: PMC111668
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1900-1907.2000
Modulation of major histocompatibility class II protein expression by varicella-zoster virus
Abstract
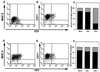
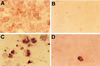
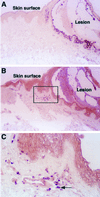
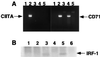
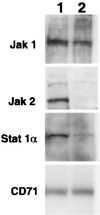
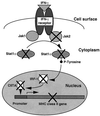
We sought to investigate the effects of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection on gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-stimulated expression of cell surface major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules on human fibroblasts. IFN-gamma treatment induced cell surface MHC class II expression on 60 to 86% of uninfected cells, compared to 20 to 30% of cells which had been infected with VZV prior to the addition of IFN-gamma. In contrast, cells that were treated with IFN-gamma before VZV infection had profiles of MHC class II expression similar to those of uninfected cell populations. Neither IFN-gamma treatment nor VZV infection affected the expression of transferrin receptor (CD71). In situ and Northern blot hybridization of MHC II (MHC class II DR-alpha) RNA expression in response to IFN-gamma stimulation revealed that MHC class II DR-alpha mRNA accumulated in uninfected cells but not in cells infected with VZV. When skin biopsies of varicella lesions were analyzed by in situ hybridization, MHC class II transcripts were detected in areas around lesions but not in cells that were infected with VZV. VZV infection inhibited the expression of Stat 1alpha and Jak2 proteins but had little effect on Jak1. Analysis of regulatory events in the IFN-gamma signaling pathway showed that VZV infection inhibited transcription of interferon regulatory factor 1 and the MHC class II transactivator. This is the first report that VZV encodes an immunomodulatory function which directly interferes with the IFN-gamma signal transduction via the Jak/Stat pathway and enables the virus to inhibit IFN-gamma induction of cell surface MHC class II expression. This inhibition of MHC class II expression on VZV-infected cells in vivo may transiently protect cells from CD4(+) T-cell immune surveillance, facilitating local virus replication and transmission during the first few days of cutaneous lesion formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of gamma interferon-induced major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression by Porphyromonas gingivalis membrane vesicles.Infect Immun. 2002 Mar;70(3):1185-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.3.1185-1192.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11854199 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon (IFN) beta acts downstream of IFN-gamma-induced class II transactivator messenger RNA accumulation to block major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression and requires the 48-kD DNA-binding protein, ISGF3-gamma.J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1517-25. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1517. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7595221 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta attenuates the class II transactivator and reveals an accessory pathway of IFN-gamma action.J Immunol. 1997 Feb 1;158(3):1095-101. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9013947
-
Immune evasion mechanisms of varicella-zoster virus.Arch Virol Suppl. 2001;(17):99-107. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6259-0_11. Arch Virol Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11339556 Review.
-
Varicella-zoster virus immune evasion.Immunol Rev. 1999 Apr;168:143-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01289.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10399071 Review.
Cited by
-
Varicella Zoster Virus Downregulates Expression of the Nonclassical Antigen Presentation Molecule CD1d.J Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 16;230(2):e416-e426. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad512. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37972257 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell immunity to human alphaherpesviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2013 Aug;3(4):452-60. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 May 8. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23664660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon Regulatory Factors 1 and 2 Play Different Roles in MHC II Expression Mediated by CIITA in Grass Carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella.Front Immunol. 2019 May 22;10:1106. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01106. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31191518 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Related Gene Expression Patterns in GPV- or H9N2-Infected Goose Spleens.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 1;17(12):1990. doi: 10.3390/ijms17121990. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27916934 Free PMC article.
-
The MHC Class II Transactivator CIITA: Not (Quite) the Odd-One-Out Anymore among NLR Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 22;22(3):1074. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031074. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33499042 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abendroth A, Arvin A M. Varicella-zoster virus immune evasion. Immunol Rev. 1999;168:143–156. - PubMed
-
- Arvin A M, Kushner J H, Feldman S, Baehner R L, Hammond D, Merigan T C. Human leukocyte interferon for the treatment of varicella in children with cancer. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:761–765. - PubMed
-
- Arvin A M, Koropchak C M, Williams B R, Grumet F C, Foung S K. Early immune response in healthy and immunocompromised subjects with primary varicella-zoster virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1986;154:422–429. - PubMed
-
- Arvin A. Varicella-zoster virus. In: Fields B, Knipe D, Howley P, editors. Fields virology. New York, N.Y: Raven; 1995. pp. 2547–2586.
-
- Arvin A. Varicella-zoster virus: virologic and immunologic aspects of persistent infection. In: Ahmed R, Chen I, editors. Persistent viral infections. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.; 1998. pp. 183–208.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

