Mcl-1 deficiency results in peri-implantation embryonic lethality
- PMID: 10640272
- PMCID: PMC316347
Mcl-1 deficiency results in peri-implantation embryonic lethality
Abstract
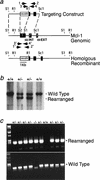
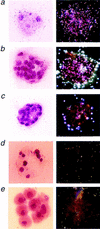
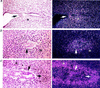
We disrupted the Mcl-1 locus in murine ES cells to determine the developmental roles of this Bcl-2 family member. Deletion of Mcl-1 resulted in peri-implantation embryonic lethality. Mcl-1(-/-) embryos do not implant in utero, but could be recovered at E3.5-4.0. Null blastocysts failed to hatch or attach in vitro, indicating a trophectoderm defect, although the inner cell mass could grow in culture. Of note, Mcl-1(-/-) blastocysts showed no evidence of increased apoptosis, but exhibited a delay in maturation beyond the precompaction stage. This model indicates that Mcl-1 is essential for preimplantation development and implantation, and suggests that it has a function beyond regulating apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Developmental changes in expression of myeloid cell leukemia-1 in human germ cells during oogenesis and early folliculogenesis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jul;87(7):3417-27. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.7.8644. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12107261
-
Developmental analysis of the Hba(th-J) mouse mutation: effects on mouse peri-implantation development and identification of two candidate genes.Dev Biol. 1995 Nov;172(1):253-63. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.0020. Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 7589805
-
Characterization of the antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family member myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) and the stimulation of its message by gonadotropins in the rat ovary.Endocrinology. 1999 Dec;140(12):5469-77. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.12.7171. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10579309
-
Physiological Functions of Mcl-1: Insights From Genetic Mouse Models.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 16;9:704547. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.704547. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34336857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic regulation of embryo death and senescence.Theriogenology. 2001 Jan 1;55(1):171-91. doi: 10.1016/s0093-691x(00)00453-2. Theriogenology. 2001. PMID: 11198081 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of MCL-1 causes lethal cardiac failure and mitochondrial dysfunction.Genes Dev. 2013 Jun 15;27(12):1351-64. doi: 10.1101/gad.215855.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 23788622 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-xL Is Essential for the Survival and Function of Differentiated Neurons in the Cortex That Control Complex Behaviors.J Neurosci. 2016 May 18;36(20):5448-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4247-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27194326 Free PMC article.
-
The double life of MULE in preeclamptic and IUGR placentae.Cell Death Dis. 2012 May 3;3(5):e305. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.44. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22552282 Free PMC article.
-
ELK4 neutralization sensitizes glioblastoma to apoptosis through downregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1.Neuro Oncol. 2011 Nov;13(11):1202-12. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nor119. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Neuro Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21846680 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Mcl-1 promotes T lymphocyte survival at multiple stages.J Immunol. 2008 Jul 1;181(1):521-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.1.521. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18566418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrendtsen O, Werb Z. Metalloproteinases regulate parietal endoderm differentiating and migrating in cultured mouse embryos. Dev Dyn. 1997;208:255–265. - PubMed
-
- Bodrug SE, Aime-Sempe C, Sato T, Krajewski S, Hanada M, Reed JC. Biochemical and functional comparisons of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 proteins: Evidence for a novel mechanism of regulating Bcl-2 family protein function. Cell Death Differ. 1995;2:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Deckwerth TL, Elliott JL, Knudson CM, Johnson EM, Jr, Snider WD, Korsmeyer SJ. BAX is required for neuronal death after trophic factor deprivation and during development. Neuron. 1996;17:401–411. - PubMed
-
- El-Shershaby AM, Hinchliffe JR. Cell redundancy in the zona-intact preimplantation mouse blastocyst: A light and electron microscope study of dead cells and their fate. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1974;31:643–654. - PubMed
-
- Fassler R, Meyer M. Consequences of lack of β 1 integrin gene expression in mice. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:1896–1908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
