Dual palmitoylation of PSD-95 mediates its vesiculotubular sorting, postsynaptic targeting, and ion channel clustering
- PMID: 10629226
- PMCID: PMC2156213
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.148.1.159
Dual palmitoylation of PSD-95 mediates its vesiculotubular sorting, postsynaptic targeting, and ion channel clustering
Abstract
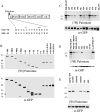
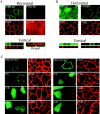
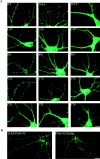
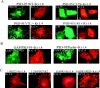
Postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95/SAP-90) is a palmitoylated peripheral membrane protein that scaffolds ion channels at excitatory synapses. To elucidate mechanisms for postsynaptic ion channel clustering, we analyzed the cellular trafficking of PSD-95. We find that PSD-95 transiently associates with a perinuclear membranous compartment and traffics with vesiculotubular structures, which migrate in a microtubule-dependent manner. Trafficking of PSD-95 with these vesiculotubular structures requires dual palmitoylation, which is specified by five consecutive hydrophobic residues at the NH(2) terminus. Mutations that disrupt dual palmitoylation of PSD-95 block both ion channel clustering by PSD-95 and its synaptic targeting. Replacing the palmitoylated NH(2) terminus of PSD-95 with alternative palmitoylation motifs at either the NH(2) or COOH termini restores ion channel clustering also induces postsynaptic targeting, respectively. In brain, we find that PSD-95 occurs not only at PSDs but also in association with intracellular smooth tubular structures in dendrites and spines. These data imply that PSD-95 is an itinerant vesicular protein; initial targeting of PSD-95 to an intracellular membrane compartment may participate in postsynaptic ion channel clustering by PSD-95.
Figures
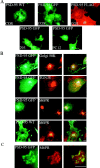
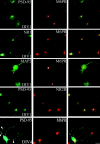
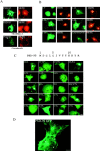
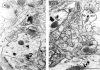
Similar articles
-
Ion channel clustering by membrane-associated guanylate kinases. Differential regulation by N-terminal lipid and metal binding motifs.J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 4;275(31):23904-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M909919199. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10779526
-
PSD-95 and SAP97 exhibit distinct mechanisms for regulating K(+) channel surface expression and clustering.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jan 10;148(1):147-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.1.147. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10629225 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal inwardly rectifying K(+) channels differentially couple to PDZ proteins of the PSD-95/SAP90 family.J Neurosci. 2000 Jan 1;20(1):156-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-01-00156.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10627592 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic targeting of the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 mediated by lipid and protein motifs.Neuron. 1999 Mar;22(3):497-509. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80705-9. Neuron. 1999. PMID: 10197530
-
Clustering of Shaker-type K+ channels by interaction with a family of membrane-associated guanylate kinases.Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):85-8. doi: 10.1038/378085a0. Nature. 1995. PMID: 7477295
Cited by
-
The Dual PDZ Domain from Postsynaptic Density Protein 95 Forms a Scaffold with Peptide Ligand.Biophys J. 2020 Aug 4;119(3):667-689. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.06.018. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32652058 Free PMC article.
-
PDZ domain-mediated interactions of G protein-coupled receptors with postsynaptic density protein 95: quantitative characterization of interactions.PLoS One. 2013 May 14;8(5):e63352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063352. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691031 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of PSD-95 Depalmitoylating Enzymes.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 15;36(24):6431-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0419-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27307232 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol up-regulates the synaptic expression of the nuclear translational regulatory protein AIDA-1 in primary hippocampal neurons.Alcohol. 2012 Sep;46(6):569-76. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2012.04.004. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22703994 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular association of glycine receptor with gephyrin increases its plasma membrane accumulation rate.J Neurosci. 2004 Feb 4;24(5):1119-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4380-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14762130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoki C., Bredt D.S., Fenstemaker S., Lubin M. The subcellular distribution of nitric oxide synthase relative to the NR1 subunit of NMDA receptors in the cerebral cortex. Prog. Brain Research. 1998;118:83–97. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C., Oviedo H., Alexandre L., Bredt D.S. Synaptic membranous and cytoplasmic localization of PSD-95EM-immunocytochemical detection with intact developing cortical neuropil Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 510.8 1999. 1277a
-
- Arnold D.B., Clapham D.E. Molecular determinants for subcellular localization of PSD-95 with an interacting K+ channel. Neuron. 1999;23:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Brenman J.E., Chao D.S., Gee S.H., McGee A.W., Craven S.E., Santillano D.R., Huang F., Xia H., Peters M.F., Froehner S.C., Bredt D.S. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and α-1 syntrophin mediated by PDZ motifs Cell 84 1996. 757 767a - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

