Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane
- PMID: 10629050
- PMCID: PMC85210
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.3.929-935.2000
Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane
Abstract
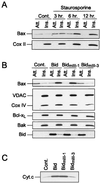
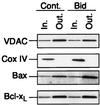
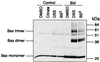
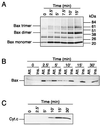
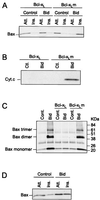
In many types of apoptosis, the proapoptotic protein Bax undergoes a change in conformation at the level of the mitochondria. This event always precedes the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c, which, in the cytosol, activates caspases through binding to Apaf-1. The mechanisms by which Bax triggers cytochrome c release are unknown. Here we show that following binding to the BH3-domain-only proapoptotic protein Bid, Bax oligomerizes and then integrates in the outer mitochondrial membrane, where it triggers cytochrome c release. Bax mitochondrial membrane insertion triggered by Bid may represent a key step in pathways leading to apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Bax-induced cytochrome c release from neural cell and brain mitochondria by dibucaine and propranolol.J Neurosci. 2003 Apr 1;23(7):2735-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02735.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12684459 Free PMC article.
-
Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis.J Cell Biol. 1999 Mar 8;144(5):891-901. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.5.891. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10085289 Free PMC article.
-
Preservation of mitochondrial structure and function after Bid- or Bax-mediated cytochrome c release.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 4;150(5):1027-36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1027. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10973993 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID, which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release of cytochrome c.Cell Death Differ. 2000 Dec;7(12):1166-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400783. Cell Death Differ. 2000. PMID: 11175253 Review.
-
Bax, Bid and the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane in apoptosis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;12(4):414-9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00110-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10873816 Review.
Cited by
-
Cathepsin B launches an apoptotic exit effort upon cell death-associated disruption of lysosomes.Cell Death Discov. 2016 Feb 29;2:16012. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.12. eCollection 2016. Cell Death Discov. 2016. PMID: 27551506 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-xL mutant promotes cartilage differentiation of BMSCs by upregulating TGF-β/BMP expression levels.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):736. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10168. Epub 2021 May 9. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34055053 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress-Induced Unscheduled CDK1-Cyclin B1 Activity Impairs ER-Mitochondria-Mediated Bioenergetic Metabolism.Cells. 2021 May 21;10(6):1280. doi: 10.3390/cells10061280. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34064109 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between age at menarche and breast cancer in individuals, as well as in first-degree kin and estrogen receptor status: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 14;14:1408132. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1408132. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38947899 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of the TRAIL/Apo2L apoptotic pathway by histone deacetylase inhibitors: an attractive approach to bypass melanoma immunotherapy resistance.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Feb 27;2(1):55-74. Print 2013. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23885325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J M, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A M, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod J-J, Mazzei G, Maundrell K, Gambale F, Sadoul R, Martinou J-C. Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science. 1997;277:370–372. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
