p53 mutants have selective dominant-negative effects on apoptosis but not growth arrest in human cancer cell lines
- PMID: 10629033
- PMCID: PMC85193
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.3.770-778.2000
p53 mutants have selective dominant-negative effects on apoptosis but not growth arrest in human cancer cell lines
Abstract
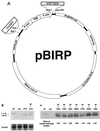
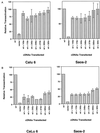
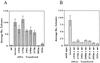
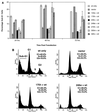
A bidirectional expression vector that allowed equal transcription of cloned wild-type and mutant p53 cDNAs from the same vector was developed. The vector was transfected into CaLu 6 lung carcinoma cells or Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells. All p53 mutants examined were recessive to wild-type p53 transactivation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) but dominant-negative for transactivation of Bax. An examination of effects on growth arrest and apoptotic pathways indicated that all mutants were recessive to wild type for growth arrest but only three of seven mutants were dominant negative for induction of apoptosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of differential activation of target gene promoters by p53 hinge domain mutants with impaired apoptotic function.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 31;276(35):32990-3000. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103681200. Epub 2001 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11395510
-
Modulation of wild-type p53 activity by mutant p53 R273H depends on the p53 responsive element (p53RE). A comparative study between the p53REs of the MDM2, WAFI/Cip1 and Bax genes in the lung cancer environment. WAFI/Cip1 = WAF1/Cip1.Anticancer Res. 1999 Jan-Feb;19(1A):579-87. Anticancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10226602
-
Expression of cell-cycle mediators in ovarian cancer cells after transfection with p16(INK4a), p21(WAF1/Cip-1), and p53.Gynecol Oncol. 2001 Dec;83(3):543-8. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2001.6438. Gynecol Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11733969
-
Induction of apoptosis by the p53-273L (Arg --> Leu) mutant in HSC3 cells without transactivation of p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 and bax.Mol Carcinog. 1999 Sep;26(1):44-52. Mol Carcinog. 1999. PMID: 10487521
-
p53 mutants can often transactivate promoters containing a p21 but not Bax or PIG3 responsive elements.Oncogene. 2001 Jun 14;20(27):3573-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204468. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11429705
Cited by
-
Selective cytotoxicity of intracellular amyloid beta peptide1-42 through p53 and Bax in cultured primary human neurons.J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 4;156(3):519-29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110119. Epub 2002 Jan 28. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11815632 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic modeling of Li-Fraumeni syndrome in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2010 Jan-Feb;3(1-2):45-56. doi: 10.1242/dmm.003749. Dis Model Mech. 2010. PMID: 20075382 Free PMC article.
-
p53 tetramerization: at the center of the dominant-negative effect of mutant p53.Genes Dev. 2020 Sep 1;34(17-18):1128-1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.340976.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32873579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of febrile temperature on adenoviral infection and replication: implications for viral therapy of cancer.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):581-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.581-591.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596850 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism seeking long term association with complex disease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Aug 1;30(15):3295-311. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkf466. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12140314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aurelio O N, Cajot J F, Hua M L, Khwaja Z, Stanbridge E J. Germ-line-derived hinge domain p53 mutants have lost apoptotic but not cell cycle arrest functions. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2190–2195. - PubMed
-
- Bader S A, Fasching C, Brodeur G M, Stanbridge E J. Dissociation of suppression of tumorigenicity and differentiation in vitro effected by transfer of single human chromosomes into human neuroblastoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991;2:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Boukamp P, Peter W, Pascheberg U, Altmeier S, Fasching C, Stanbridge E J, Fusenig N E. Step-wise progression in human skin carcinogenesis in vitro involves mutational inactivation of p53, rasH oncogene activation and additional chromosome loss. Oncogene. 1995;11:961–969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
