The cAMP receptor protein CRP can function as an osmoregulator of transcription in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 10601034
- PMCID: PMC317180
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.23.3081
The cAMP receptor protein CRP can function as an osmoregulator of transcription in Escherichia coli
Erratum in
- Genes Dev 2000 Feb 1;14(3):389
Abstract
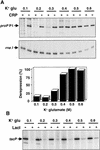
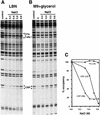
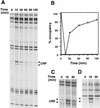
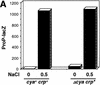
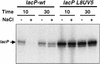
Transcription of the P1 promoter of the Escherichia coli proP gene, which encodes a transporter of osmoprotectants, is strongly induced by a shift to hyperosmotic media. Unlike most other osmotically regulated promoters, the induction occurs for a brief period of time, corresponding to the replacement of intracellular K(+) glutamate with osmoprotecting compounds. This burst of proP transcription is correlated with the osmolarity-dependent binding of the cAMP receptor protein CRP to a site within the proP P1 promoter. We show that CRP-cAMP functions as an osmotically sensitive repressor of proP P1 transcription in vitro. Binding of CRP to the proP promoter in vivo is transiently destabilized after a hyperosmotic shift with kinetics that correspond to the derepression of transcription, whereas Fis and Lac repressor binding is not osmotically sensitive. Similar osmotic regulation of proP P1 transcription by the CRP* mutant implies that binding of cAMP is not responsible for the unusual osmotic sensitivity of CRP activity. Osmotic regulation of CRP activity is not limited to proP. Activation of the lac promoter by CRP is also transiently inhibited after an osmotic upshift, as is the binding of CRP to the galdelta4P1 promoter. These findings suggest that CRP functions in certain contexts to regulate gene expression in response to osmotic changes, in addition to its role in catabolite control.
Figures
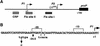





Similar articles
-
Cyclic AMP receptor protein functions as a repressor of the osmotically inducible promoter proP P1 in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1997 Apr;179(7):2410-7. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.7.2410-2417.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9079929 Free PMC article.
-
Fis activates the RpoS-dependent stationary-phase expression of proP in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1995 Sep;177(18):5222-31. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.18.5222-5231.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7545153 Free PMC article.
-
Complex transcriptional control of the sigma s-dependent stationary-phase-induced and osmotically regulated osmY (csi-5) gene suggests novel roles for Lrp, cyclic AMP (cAMP) receptor protein-cAMP complex, and integration host factor in the stationary-phase response of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7910-7. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7910-7917.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8253679 Free PMC article.
-
How is osmotic regulation of transcription of the Escherichia coli proU operon achieved? A review and a model.Genetica. 1996 May;97(3):363-78. doi: 10.1007/BF00055322. Genetica. 1996. PMID: 9081863 Review.
-
A flexible partnership: the CytR anti-activator and the cAMP-CRP activator protein, comrades in transcription control.Mol Microbiol. 1996 May;20(3):461-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.5341056.x. Mol Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8736525 Review.
Cited by
-
Tinkering with Osmotically Controlled Transcription Allows Enhanced Production and Excretion of Ectoine and Hydroxyectoine from a Microbial Cell Factory.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jan 2;84(2):e01772-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01772-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29101191 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of salt shock on stability of lambdaimm434 lysogens.J Bacteriol. 2007 Apr;189(8):3115-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01857-06. Epub 2007 Feb 16. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17307857 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling early osmostress-dependent gene expression in Escherichia coli using DNA macroarrays.J Bacteriol. 2002 Oct;184(19):5502-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.19.5502-5507.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12218039 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli non-coding regulatory regions are highly conserved.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 May 20;6(2):lqae041. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae041. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38774514 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of the osmoregulated promoter-derived proP mRNA is posttranscriptionally regulated by RNase III in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2015 Apr;197(7):1297-305. doi: 10.1128/JB.02460-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25645556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Booth IR, Higgins CF. Enteric bacteria and osmotic stress: Intracellular potassium glutamate as a secondary signal of osmotic stress? FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990;6:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Burgess RR, Jendrisak JJ. A procedure for the rapid, large-scale purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975;14:4634–4638. - PubMed
-
- Case CC, Roels SM, Gonzalez JE, Simons EL, Simons RW. Analysis of the promoters and transcripts involved in IS10 anti-sense RNA control. Gene. 1988;72:219–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
