An Eph receptor regulates integrin activity through R-Ras
- PMID: 10570155
- PMCID: PMC24147
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.24.13813
An Eph receptor regulates integrin activity through R-Ras
Abstract
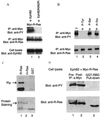
The ability of integrins to mediate cell attachment to extracellular matrices and to blood proteins is regulated from inside the cell. Increased ligand-binding activity of integrins is critical for platelet aggregation upon blood clotting and for leukocyte extravasation to inflamed tissues. Decreased adhesion is thought to promote tumor cell invasion. R-Ras, a small intracellular GTPase, regulates the binding of integrins to their ligands outside the cell. Here we show that the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase, EphB2, can control integrin activity through R-Ras. Cells in which EphB2 is activated become poorly adherent to substrates coated with integrin ligands, and a tyrosine residue in the R-Ras effector domain is phosphorylated. The R-Ras phosphorylation and loss of cell adhesion are causally related, because forced expression of an R-Ras variant resistant to phosphorylation at the critical site made cells unresponsive to the anti-adhesive effect of EphB2. This is an unusual regulatory pathway among the small GTPases. Reduced adhesiveness induced through the Eph/R-Ras pathway may explain the repulsive effect of the Eph receptors in axonal pathfinding and may facilitate tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis.
Figures

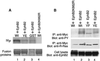


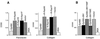
Similar articles
-
EphB2/R-Ras signaling regulates glioma cell adhesion, growth, and invasion.Am J Pathol. 2005 Aug;167(2):565-76. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62998-7. Am J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16049340 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by the EphB2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for ephrin-induced neurite retraction.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Nov;21(21):7429-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7429-7441.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11585923 Free PMC article.
-
Activated SRC oncogene phosphorylates R-ras and suppresses integrin activity.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 18;277(3):1824-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103133200. Epub 2001 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11682467
-
Reprint of Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24263067 Review.
-
Integrins in cell adhesion and signaling.Hum Cell. 1996 Sep;9(3):181-6. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183647 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Small and Large Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Reveals Enrichment of Adhesion Proteins in Small EVs.J Proteome Res. 2019 Mar 1;18(3):947-959. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00647. Epub 2019 Jan 23. J Proteome Res. 2019. PMID: 30608700 Free PMC article.
-
Eph kinases and ephrins support thrombus growth and stability by regulating integrin outside-in signaling in platelets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jul 12;102(28):9820-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404065102. Epub 2005 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15994237 Free PMC article.
-
Eph/ephrin signaling: networks.Genes Dev. 2008 Feb 15;22(4):416-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.1630408. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18281458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular interactions of EphA4, growth hormone receptor, Janus kinase 2, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 7;12(7):e0180785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180785. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28686668 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of phosphotyrosine binding domain-containing proteins as novel downstream targets of the EphA8 signaling function.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;27(23):8113-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00794-07. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17875921 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

