Roles of bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors and Smad proteins in osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation
- PMID: 10564272
- PMCID: PMC25680
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.11.3801
Roles of bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors and Smad proteins in osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation
Abstract
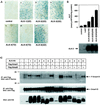
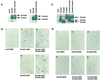
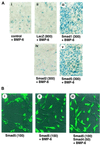
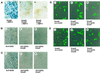
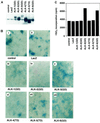
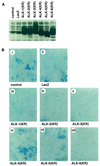
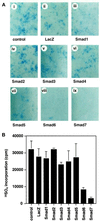
The biological effects of type I serine/threonine kinase receptors and Smad proteins were examined using an adenovirus-based vector system. Constitutively active forms of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I receptors (BMPR-IA and BMPR-IB; BMPR-I group) and those of activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)-1 and ALK-2 (ALK-1 group) induced alkaline phosphatase activity in C2C12 cells. Receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads) that act in the BMP pathways, such as Smad1 and Smad5, also induced the alkaline phosphatase activity in C2C12 cells. BMP-6 dramatically enhanced alkaline phosphatase activity induced by Smad1 or Smad5, probably because of the nuclear translocation of R-Smads triggered by the ligand. Inhibitory Smads, i.e., Smad6 and Smad7, repressed the alkaline phosphatase activity induced by BMP-6 or the type I receptors. Chondrogenic differentiation of ATDC5 cells was induced by the receptors of the BMPR-I group but not by those of the ALK-1 group. However, kinase-inactive forms of the receptors of the ALK-1 and BMPR-I groups blocked chondrogenic differentiation. Although R-Smads failed to induce cartilage nodule formation, inhibitory Smads blocked it. Osteoblast differentiation induced by BMPs is thus mediated mainly via the Smad-signaling pathway, whereas chondrogenic differentiation may be transmitted by Smad-dependent and independent pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of different bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors on alkaline phosphatase induction.J Cell Sci. 2001 Apr;114(Pt 8):1483-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.8.1483. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11282024
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in articular chondrocyte differentiation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Feb 7;301(2):617-22. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)03068-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12565908
-
Requirement of BMP-2-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt serine/threonine kinase in osteoblast differentiation and Smad-dependent BMP-2 gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 6;277(36):33361-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205053200. Epub 2002 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12084724
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
TGF-beta signaling by Smad proteins.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Mar-Jun;11(1-2):15-22. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00025-8. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10708949 Review.
Cited by
-
Addition of bone morphogenetic protein type 2 to ascorbate and β-glycerophosphate supplementation did not enhance osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells.J Appl Oral Sci. 2012 Nov-Dec;20(6):628-35. doi: 10.1590/s1678-77572012000600007. J Appl Oral Sci. 2012. PMID: 23329244 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Jun 1;8(6):a021899. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021899. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27252362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of bone development and repair.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Nov;21(11):696-711. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00279-w. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32901139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noggin overexpression inhibits eyelid opening by altering epidermal apoptosis and differentiation.EMBO J. 2003 Jun 16;22(12):2992-3003. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg291. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12805214 Free PMC article.
-
Osteocyte control of bone formation via sclerostin, a novel BMP antagonist.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 1;22(23):6267-76. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg599. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14633986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama S, Katagiri T, Namiki M, Yamaji N, Yamamoto N, Miyama K, Shibuya H, Ueno N, Wozney JM, Suda T. Constitutively active BMP type I receptors transduce BMP-2 signals without the ligand in C2C12 myoblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1997;235:362–369. - PubMed
-
- Armes NA, Neal KA, Smith JC. A short loop on the ALK-2 and ALK-4 activin receptors regulates signaling specificity but cannot account for all their effects on early Xenopus development. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:7929–7935. - PubMed
-
- Armes NA, Smith JC. The ALK-2 and ALK-4 activin receptors transduce distinct mesoderm-inducing signals during early Xenopus development but do not cooperate to establish thresholds. Development. 1997;124:3797–3804. - PubMed
-
- Asahina I, Sampath TK, Hauschka PV. Human osteogenic protein-1 induces chondroblastic, osteoblastic, and/or adipocytic differentiation of clonal murine target cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996;222:38–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

