Identification of an ATP-binding cassette transporter involved in bicarbonate uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942
- PMID: 10557362
- PMCID: PMC23989
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13571
Identification of an ATP-binding cassette transporter involved in bicarbonate uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942
Abstract
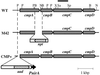
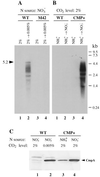
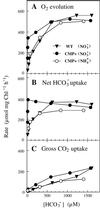
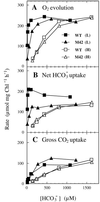
Exposure of cells of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) grown under high-CO(2) conditions to inorganic C-limitation induces transcription of particular genes and expression of high-affinity CO(2) and HCO(3)(-) transport systems. Among the low-CO(2)-inducible transcription units of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 is the cmpABCD operon, encoding an ATP-binding cassette transporter similar to the nitrate/nitrite transporter of the same cyanobacterium. A nitrogen-regulated promoter was used to selectively induce expression of the cmpABCD genes by growth of transgenic cells on nitrate under high CO(2) conditions. Measurements of the initial rate of HCO(3)(-) uptake after onset of light, and of the steady-state rate of HCO(3)(-) uptake in the light, showed that the controlled induction of the cmp genes resulted in selective expression of high-affinity HCO(3)(-) transport activity. The forced expression of cmpABCD did not significantly increase the CO(2) uptake capabilities of the cells. These findings demonstrated that the cmpABCD genes encode a high-affinity HCO(3)(-) transporter. A deletion mutant of cmpAB (M42) retained low CO(2)-inducible activity of HCO(3)(-) transport, indicating the occurrence of HCO(3)(-) transporter(s) distinct from the one encoded by cmpABCD. HCO(3)(-) uptake by low-CO(2)-induced M42 cells showed lower affinity for external HCO(3)(-) than for wild-type cells under the same conditions, showing that the HCO(3)(-) transporter encoded by cmpABCD has the highest affinity for HCO(3)(-) among the HCO(3)(-) transporters present in the cyanobacterium. This appears to be the first unambiguous identification and description of a primary active HCO(3)(-) transporter.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bicarbonate binding activity of the CmpA protein of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 involved in active transport of bicarbonate.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 7;275(27):20551-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003034200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10779519
-
Involvement of a CbbR homolog in low CO2-induced activation of the bicarbonate transporter operon in cyanobacteria.J Bacteriol. 2001 Mar;183(6):1891-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.6.1891-1898.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11222586 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the C-terminal domain of an ATP-binding subunit in the regulation of the ABC-type nitrate/nitrite transporter of the Cyanobacterium synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942.J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 24;272(43):27197-201. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.43.27197. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9341163
-
Structure, function and regulation of the nitrate transport system of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7942.Plant Cell Physiol. 1995 Mar;36(2):207-13. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078751. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7767600 Review.
-
Transport and Use of Bicarbonate in Plants: Current Knowledge and Challenges Ahead.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 3;19(5):1352. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051352. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29751549 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism underlying transport and allosteric inhibition of bicarbonate transporter SbtA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 1;118(22):e2101632118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101632118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34031249 Free PMC article.
-
A PII-Like Protein Regulated by Bicarbonate: Structural and Biochemical Studies of the Carboxysome-Associated CPII Protein.J Mol Biol. 2016 Oct 9;428(20):4013-4030. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27464895 Free PMC article.
-
In search of the pH limit of growth in halo-alkaliphilic cyanobacteria.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2024 Aug;16(4):e13323. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.13323. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39128846 Free PMC article.
-
Sensing of inorganic carbon limitation in Synechococcus PCC7942 is correlated with the size of the internal inorganic carbon pool and involves oxygen.Plant Physiol. 2005 Dec;139(4):1959-69. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.069146. Epub 2005 Nov 23. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16306144 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and functional roles of the two distinct NDH-1 complexes and the carbon acquisition complex NdhD3/NdhF3/CupA/Sll1735 in Synechocystis sp PCC 6803.Plant Cell. 2004 Dec;16(12):3326-40. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026526. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15548742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaplan A, Schwarz R, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Ronen-Tarazi M, Reinhold L. In: The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria. Bryant D A, editor. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer; 1994. pp. 469–485.
-
- Price G D, Sültemeyer D, Klughammer B, Ludwig M, Badger M R. Can J Bot. 1998;76:973–1002.
-
- Bonfil D J, Tarazi-Ronen M, Sültemeyer D, Lieman-Hurwitz J, Schatz D, Kaplan A. FEBS Lett. 1998;430:236–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

