Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 10557268
- PMCID: PMC23895
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13034
Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus
Abstract
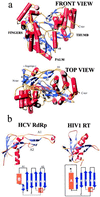
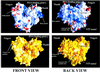
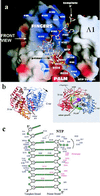
We report the crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus, a major human pathogen, to 2.8-A resolution. This enzyme is a key target for developing specific antiviral therapy. The structure of the catalytic domain contains 531 residues folded in the characteristic fingers, palm, and thumb subdomains. The fingers subdomain contains a region, the "fingertips," that shares the same fold with reverse transcriptases. Superposition to the available structures of the latter shows that residues from the palm and fingertips are structurally equivalent. In addition, it shows that the hepatitis C virus polymerase was crystallized in a closed fingers conformation, similar to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in ternary complex with DNA and dTTP [Huang H., Chopra, R., Verdine, G. L. & Harrison, S. C. (1998) Science 282, 1669-1675]. This superposition reveals the majority of the amino acid residues of the hepatitis C virus enzyme that are likely to be implicated in binding to the replicating RNA molecule and to the incoming NTP. It also suggests a rearrangement of the thumb domain as well as a possible concerted movement of thumb and fingertips during translocation of the RNA template-primer in successive polymerization rounds.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from bovine viral diarrhea virus establishes the role of GTP in de novo initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 30;101(13):4425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400660101. Epub 2004 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15070734 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of an N-terminal fragment from Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase complexed with nucleic acid: functional implications for template-primer binding to the fingers domain.J Mol Biol. 2000 Feb 18;296(2):613-32. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3477. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10669612
-
Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus.Structure. 1999 Nov 15;7(11):1417-26. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)80031-3. Structure. 1999. PMID: 10574802
-
Recent advances in the analysis of HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2000 Nov;1(3):289-96. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2000. PMID: 11249710 Review.
-
Protein-nucleic acid interactions and DNA conformation in a complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase with a double-stranded DNA template-primer.Biopolymers. 1997;44(2):125-38. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1997)44:2<125::AID-BIP2>3.0.CO;2-X. Biopolymers. 1997. PMID: 9354757 Review.
Cited by
-
Thumb inhibitor binding eliminates functionally important dynamics in the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase.Proteins. 2013 Jan;81(1):40-52. doi: 10.1002/prot.24154. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Proteins. 2013. PMID: 22855387 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoinformatics approach for investigation of alternative potential hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5B inhibitors.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 27;9:1825-41. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S75886. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25848219 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and biochemical diversity in the HCV NS5B RNA polymerase in the context of interferon α plus ribavirin therapy.J Viral Hepat. 2011 May;18(5):349-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01316.x. J Viral Hepat. 2011. PMID: 20529202 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from bovine viral diarrhea virus establishes the role of GTP in de novo initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 30;101(13):4425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400660101. Epub 2004 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15070734 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the autophagy machinery on hepatitis C virus infection.Viruses. 2011 Aug;3(8):1342-57. doi: 10.3390/v3081342. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994783 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rice C M. In: Virology. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, Chanock R M, Melnick J L, Monath T P, Roizman B, Straus S E, editors. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1996. pp. 931–959.
-
- Ollis D L, Brick P, Hamlin R, Xuong N G, Steitz T A. Nature (London) 1985;313:762–766. - PubMed
-
- Brautigam C A, Steitz T A. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:54–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

