Genetic characterization of the major lactococcal aromatic aminotransferase and its involvement in conversion of amino acids to aroma compounds
- PMID: 10543798
- PMCID: PMC91656
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.4873-4880.1999
Genetic characterization of the major lactococcal aromatic aminotransferase and its involvement in conversion of amino acids to aroma compounds
Abstract
In lactococci, transamination is the first step of the enzymatic conversion of aromatic and branched-chain amino acids to aroma compounds. In previous work we purified and biochemically characterized the major aromatic aminotransferase (AraT) of a Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris strain. Here we characterized the corresponding gene and evaluated the role of AraT in the biosynthesis of amino acids and in the conversion of amino acids to aroma compounds. Amino acid sequence homologies with other aminotransferases showed that the enzyme belongs to a new subclass of the aminotransferase I subfamily gamma; AraT is the best-characterized representative of this new aromatic-amino-acid-specific subclass. We demonstrated that AraT plays a major role in the conversion of aromatic amino acids to aroma compounds, since gene inactivation almost completely prevented the degradation of these amino acids. It is also highly involved in methionine and leucine conversion. AraT also has a major physiological role in the biosynthesis of phenylalanine and tyrosine, since gene inactivation weakly slowed down growth on medium without phenylalanine and highly affected growth on every medium without tyrosine. However, another biosynthesis aromatic aminotransferase is induced in the absence of phenylalanine in the culture medium.
Figures

 , the region upstream of araT with two potential promoters and a potential terminator just upstream.
, the region upstream of araT with two potential promoters and a potential terminator just upstream.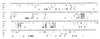
Similar articles
-
Characterization and role of the branched-chain aminotransferase (BcaT) isolated from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris NCDO 763.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Feb;66(2):571-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.2.571-577.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10653720 Free PMC article.
-
An aminotransferase from Lactococcus lactis initiates conversion of amino acids to cheese flavor compounds.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997 Feb;63(2):414-9. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.2.414-419.1997. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9023921 Free PMC article.
-
CodY-regulated aminotransferases AraT and BcaT play a major role in the growth of Lactococcus lactis in milk by regulating the intracellular pool of amino acids.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jun;69(6):3061-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.6.3061-3068.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12788699 Free PMC article.
-
Role of aminotransferase IlvE in production of branched-chain fatty acids by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jan;70(1):638-41. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.1.638-641.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14711703 Free PMC article.
-
Paracoccus denitrificans aromatic amino acid aminotransferase: a model enzyme for the study of dual substrate recognition mechanism.J Biochem. 1997 Jan;121(1):161-71. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021561. J Biochem. 1997. PMID: 9058208
Cited by
-
Probing direct interactions between CodY and the oppD promoter of Lactococcus lactis.J Bacteriol. 2005 Jan;187(2):512-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.2.512-521.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 15629923 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake of α-ketoglutarate by citrate transporter CitP drives transamination in Lactococcus lactis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Feb;79(4):1095-101. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02254-12. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23204417 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of two Lactobacillus casei genes encoding a cystathionine lyase.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jan;74(1):99-106. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00745-07. Epub 2007 Nov 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17993563 Free PMC article.
-
A microbially produced AhR ligand promotes a Tph1-driven tolerogenic program in multiple sclerosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 20;14(1):6651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57400-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38509264 Free PMC article.
-
Brevibacterium from Austrian hard cheese harbor a putative histamine catabolism pathway and a plasmid for adaptation to the cheese environment.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 16;9(1):6164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42525-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30992535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

