Structure of a soluble secreted chemokine inhibitor vCCI (p35) from cowpox virus
- PMID: 10535930
- PMCID: PMC22925
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12379
Structure of a soluble secreted chemokine inhibitor vCCI (p35) from cowpox virus
Abstract
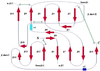
Most poxviruses, including variola, the causative agent of smallpox, express a secreted protein of 35 kDa, vCCI, which binds CC-chemokines with high affinity. This viral protein competes with the host cellular CC-chemokine receptors (CCRs), reducing inflammation and interfering with the host immune response. Such proteins or derivatives may have therapeutic uses as anti-inflammatory agents. We have determined the crystal structure to 1.85-A resolution of vCCI from cowpox virus, the prototype of this poxvirus virulence factor. The molecule is a beta-sandwich of topology not previously described. A patch of conserved residues on the exposed face of a beta-sheet that is strongly negatively charged might have a role in binding of CC-chemokines, which are positively charged.
Figures


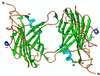
Similar articles
-
Poxvirus genomes encode a secreted, soluble protein that preferentially inhibits beta chemokine activity yet lacks sequence homology to known chemokine receptors.Virology. 1997 Sep 29;236(2):316-27. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8730. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9325239
-
Structural insights into the interaction between a potent anti-inflammatory protein, viral CC chemokine inhibitor (vCCI), and the human CC chemokine, Eotaxin-1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6592-6603. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.538991. Epub 2014 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24482230 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the complex between poxvirus-encoded CC chemokine inhibitor vCCI and human MIP-1beta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Sep 19;103(38):13985-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602142103. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16963564 Free PMC article.
-
Variola virus immune evasion proteins.Microbes Infect. 2003 Sep;5(11):1049-56. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(03)00194-1. Microbes Infect. 2003. PMID: 12941397 Review.
-
Viral chemokine-binding proteins.J Leukoc Biol. 2002 Jul;72(1):24-34. J Leukoc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12101259 Review.
Cited by
-
Subversion of cytokine networks by virally encoded decoy receptors.Immunol Rev. 2012 Nov;250(1):199-215. doi: 10.1111/imr.12009. Immunol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23046131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus encodes a highly specific RANTES decoy receptor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Nov 23;101(47):16642-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407233101. Epub 2004 Nov 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15536129 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants of chemokine binding by an Ectromelia virus-encoded decoy receptor.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7439-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00576-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840324 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving Immune Modulating Drugs from Viruses-A New Class of Biologics.J Clin Med. 2020 Mar 31;9(4):972. doi: 10.3390/jcm9040972. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32244484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How vaccinia virus has evolved to subvert the host immune response.J Struct Biol. 2011 Aug;175(2):127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.03.010. Epub 2011 Mar 17. J Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21419849 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ploegh H L. Science. 1998;280:248–253. - PubMed
-
- McFadden G, editor. Viroceptors, Virokines and Related Immune Modulators Encoded by DNA Viruses. Austin, TX: Landes; 1994.
-
- Baggiolini M. Nature (London) 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Ward S G, Bacon K, Westwick J. Immunity. 1998;9:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Springer T A. Cell. 1994;76:301–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

