Binding of integrin alpha6beta4 to plectin prevents plectin association with F-actin but does not interfere with intermediate filament binding
- PMID: 10525545
- PMCID: PMC2174221
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.2.417
Binding of integrin alpha6beta4 to plectin prevents plectin association with F-actin but does not interfere with intermediate filament binding
Abstract
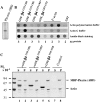
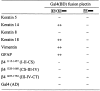
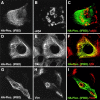
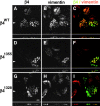
Hemidesmosomes are stable adhesion complexes in basal epithelial cells that provide a link between the intermediate filament network and the extracellular matrix. We have investigated the recruitment of plectin into hemidesmosomes by the alpha6beta4 integrin and have shown that the cytoplasmic domain of the beta4 subunit associates with an NH(2)-terminal fragment of plectin that contains the actin-binding domain (ABD). When expressed in immortalized plectin-deficient keratinocytes from human patients with epidermol- ysis bullosa (EB) simplex with muscular dystrophy (MD-EBS), this fragment is colocalized with alpha6beta4 in basal hemidesmosome-like clusters or associated with F-actin in stress fibers or focal contacts. We used a yeast two-hybrid binding assay in combination with an in vitro dot blot overlay assay to demonstrate that beta4 interacts directly with plectin, and identified a major plectin-binding site on the second fibronectin type III repeat of the beta4 cytoplasmic domain. Mapping of the beta4 and actin-binding sites on plectin showed that the binding sites overlap and are both located in the plectin ABD. Using an in vitro competition assay, we could show that beta4 can compete out the plectin ABD fragment from its association with F-actin. The ability of beta4 to prevent binding of F-actin to plectin explains why F-actin has never been found in association with hemidesmosomes, and provides a molecular mechanism for a switch in plectin localization from actin filaments to basal intermediate filament-anchoring hemidesmosomes when beta4 is expressed. Finally, by mapping of the COOH-terminally located binding site for several different intermediate filament proteins on plectin using yeast two-hybrid assays and cell transfection experiments with MD-EBS keratinocytes, we confirm that plectin interacts with different cytoskeletal networks.
Figures

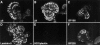
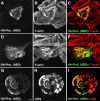
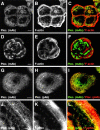

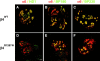

Similar articles
-
Linking integrin alpha6beta4-based cell adhesion to the intermediate filament cytoskeleton: direct interaction between the beta4 subunit and plectin at multiple molecular sites.J Cell Biol. 1998 Apr 6;141(1):209-25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.1.209. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9531560 Free PMC article.
-
A minimal region on the integrin beta4 subunit that is critical to its localization in hemidesmosomes regulates the distribution of HD1/plectin in COS-7 cells.J Cell Sci. 1997 Aug;110 ( Pt 15):1705-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110.15.1705. J Cell Sci. 1997. PMID: 9264458
-
Formation of hemidesmosome-like structures in the absence of ligand binding by the (alpha)6(beta)4 integrin requires binding of HD1/plectin to the cytoplasmic domain of the (beta)4 integrin subunit.J Cell Sci. 2000 Mar;113 ( Pt 6):963-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.6.963. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10683145
-
Plectin: a cytolinker by design.Biol Chem. 1999 Feb;380(2):151-8. doi: 10.1515/BC.1999.023. Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10195422 Review.
-
Advances and perspectives of the architecture of hemidesmosomes: lessons from structural biology.Cell Adh Migr. 2009 Oct-Dec;3(4):361-4. doi: 10.4161/cam.3.4.9525. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Cell Adh Migr. 2009. PMID: 19736524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of serine 4,642 in the C-terminus of plectin by MNK2 and PKA modulates its interaction with intermediate filaments.J Cell Sci. 2013 Sep 15;126(Pt 18):4195-207. doi: 10.1242/jcs.127779. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23843618 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of Keratins as Biomarkers for Human Oral Precancer and Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;12(3):343. doi: 10.3390/life12030343. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Imaging Conditions for Demanding Multi-Color Super Resolution Localization Microscopy.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 8;11(7):e0158884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158884. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27391487 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular distribution of envoplakin and periplakin: insights into their role as precursors of the epidermal cornified envelope.J Cell Biol. 2000 Oct 30;151(3):573-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.573. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11062259 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of TMEM268 inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells by downregulating the ITGB4 signaling pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Aug;26(8):1453-1466. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0223-3. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30361615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aho S., Uitto J. Basement membrane zone protein-protein interactions disclosed by yeast two-hybrid system. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1997;108:546a.
-
- Aho S., Uitto J. Direct interaction between the intracellular domain of bullous pemphigoid antigen 2 (BP180) and β4 integrin, hemidesmosomal components of basal keratinocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998;243:694–699. - PubMed
-
- Aho S., Uitto J. 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen/type VXII collagentissue-specific expression and molecular interactions with keratin 18. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999;72:356–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

