Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells
- PMID: 10508865
- PMCID: PMC2164984
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.1.185
Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells
Abstract
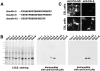
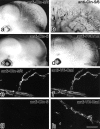
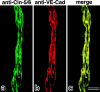
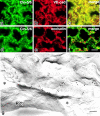
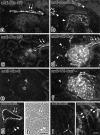
Tight junctions (TJs) in endothelial cells are thought to determine vascular permeability. Recently, claudin-1 to -15 were identified as major components of TJ strands. Among these, claudin-5 (also called transmembrane protein deleted in velo-cardio-facial syndrome [TMVCF]) was expressed ubiquitously, even in organs lacking epithelial tissues, suggesting the possible involvement of this claudin species in endothelial TJs. We then obtained a claudin-6-specific polyclonal antibody and a polyclonal antibody that recognized both claudin-5/TMVCF and claudin-6. In the brain and lung, immunofluorescence microscopy with these polyclonal antibodies showed that claudin-5/TMVCF was exclusively concentrated at cell-cell borders of endothelial cells of all segments of blood vessels, but not at those of epithelial cells. Immunoreplica electron microscopy revealed that claudin-5/TMVCF was a component of TJ strands. In contrast, in the kidney, the claudin-5/TMVCF signal was restricted to endothelial cells of arteries, but was undetectable in those of veins and capillaries. In addition, in all other tissues we examined, claudin-5/TMVCF was specifically detected in endothelial cells of some segments of blood vessels, but not in epithelial cells. Furthermore, when claudin-5/TMVCF cDNA was introduced into mouse L fibroblasts, TJ strands were reconstituted that resembled those in endothelial cells in vivo, i.e., the extracellular face-associated TJs. These findings indicated that claudin-5/TMVCF is an endothelial cell-specific component of TJ strands.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Jan 19;96(2):511-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.511. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 9892664 Free PMC article.
-
Manner of interaction of heterogeneous claudin species within and between tight junction strands.J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 15;147(4):891-903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.4.891. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10562289 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin-11/OSP-based tight junctions of myelin sheaths in brain and Sertoli cells in testis.J Cell Biol. 1999 May 3;145(3):579-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.3.579. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10225958 Free PMC article.
-
Holey barrier: claudins and the regulation of brain endothelial permeability.J Cell Biol. 2003 May 12;161(3):459-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304039. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12743096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure and function of claudins, cell adhesion molecules at tight junctions.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;915:129-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05235.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193568 Review.
Cited by
-
Claudin-1, -2, -4, and -5: comparison of expression levels and distribution in equine tissues.J Vet Sci. 2016 Dec 30;17(4):445-451. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.4.445. J Vet Sci. 2016. PMID: 27030194 Free PMC article.
-
When Innate Immunity Meets Angiogenesis-The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Endothelial Cells and Pulmonary Hypertension.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 31;7:352. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00352. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32850883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Canonical and Non-Canonical Localization of Tight Junction Proteins during Early Murine Cranial Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 24;25(3):1426. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031426. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338705 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins overexpression in ovarian cancer: potential targets for Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin (CPE) based diagnosis and therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 17;14(5):10412-37. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510412. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23685873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Major Depressive Disorder: Restoring Balance for Neuroinflammation and Neuroprotection.Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Sep 30;97(3):349-363. doi: 10.59249/YZLQ4631. eCollection 2024 Sep. Yale J Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39351324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson J.M., Van Itallie C.M. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;269:G467–G475. - PubMed
-
- Balda M.S., Whitney J.A., Flores C., González S., Cereijido M., Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J. Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bowman P.D., du Bois M., Shivers R.R., Dorovini-Zis K. Endothelial tight junctions. In: Cereijido M., editor. Tight Junctions. CRC Press; London: 1992. pp. 305–320.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

