RBP1 recruits both histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent repression activities to retinoblastoma family proteins
- PMID: 10490602
- PMCID: PMC84642
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6632
RBP1 recruits both histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent repression activities to retinoblastoma family proteins
Abstract
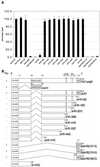
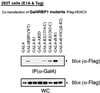
Retinoblastoma (RB) tumor suppressor family proteins block cell proliferation in part by repressing certain E2F-specific promoters. Both histone deacetylase (HDAC)-dependent and -independent repression activities are associated with the RB "pocket." The mechanism by which these two repression functions occupy the pocket is unknown. A known RB-binding protein, RBP1, was previously found by our group to be an active corepressor which, if overexpressed, represses E2F-mediated transcription via its association with the pocket. We show here that RBP1 contains two repression domains, one of which binds all three known HDACs and represses them in an HDAC-dependent manner while the other domain functions independently of the HDACs. Thus, RB family members repress transcription by recruiting RBP1 to the pocket. RBP1, in turn, serves as a bridging molecule to recruit HDACs and, in addition, provides a second HDAC-independent repression function.
Figures
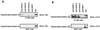





Similar articles
-
RBP1 recruits the mSIN3-histone deacetylase complex to the pocket of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor family proteins found in limited discrete regions of the nucleus at growth arrest.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;21(8):2918-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2918-2932.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11283269 Free PMC article.
-
RBP1 family proteins exhibit SUMOylation-dependent transcriptional repression and induce cell growth inhibition reminiscent of senescence.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(5):1917-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.5.1917-1931.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16479010 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription.Nature. 1998 Feb 5;391(6667):597-601. doi: 10.1038/35404. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9468139
-
[Histone deacetylase and retinoblastoma protein].Bull Cancer. 1998 Jul;85(7):606-7. Bull Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9752266 Review. French.
-
Molecular mechanisms of E2F-dependent activation and pRB-mediated repression.J Cell Sci. 2004 May 1;117(Pt 11):2173-81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01227. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15126619 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profiling of fibroblasts from a human progeroid disease (mandibuloacral dysplasia, MAD #248370) through cDNA microarrays.Gene Expr. 2004;12(1):39-47. doi: 10.3727/000000004783992189. Gene Expr. 2004. PMID: 15473259 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of chromatin remodeling genes Arid4a and Arid4b as leukemia suppressor genes.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 Sep 3;100(17):1247-59. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn253. Epub 2008 Aug 26. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008. PMID: 18728284 Free PMC article.
-
T antigens of simian virus 40: molecular chaperones for viral replication and tumorigenesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002 Jun;66(2):179-202. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.2.179-202.2002. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12040123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein targets distinct general transcription factors to regulate RNA polymerase III gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;20(24):9182-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9182-9191.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11094070 Free PMC article.
-
Role for the mortality factors MORF4, MRGX, and MRG15 in transcriptional repression via associations with Pf1, mSin3A, and Transducin-Like Enhancer of Split.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;22(22):7868-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.22.7868-7876.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12391155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adnane J, Shao Z, Robbins P D. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product represses transcription when directly bound to the promoter. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:8837–8843. - PubMed
-
- Brehm A, Miska E A, McCance D J, Reid J L, Bannister A J, Kouzarides T. Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature. 1998;391:597–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
