Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis in neurons
- PMID: 10479688
- PMCID: PMC6782440
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-18-07860.1999
Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation is a key determinant in p53-induced apoptosis in neurons
Abstract
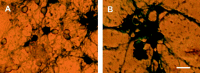
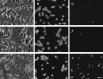
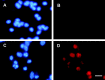
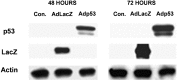
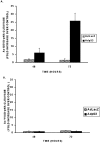
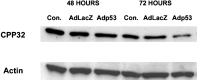
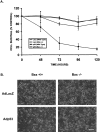
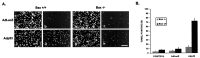
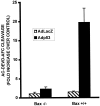
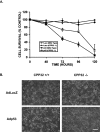
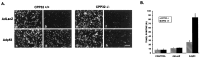
p53 is a pivotal molecule regulating the death of neurons both after acute injury and during development. The molecular mechanisms by which p53 induces apoptosis in neuronal cells, however, are not well understood. We have shown previously that adenovirus-mediated p53 gene delivery to neurons was sufficient to induce apoptosis. In the present study we have examined the molecular mechanism by which p53 evokes neuronal cell death. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of p53 to cerebellar granule neurons resulted in caspase-3 (CPP32) activation followed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated biotinylated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining and loss of viability as determined by an MTT survival assay. To determine whether Bax is essential for caspase-3 activation, p53 was expressed in Bax-deficient cells. Bax null neurons did not exhibit caspase-3 activation in response to p53 and were protected from apoptosis. To determine whether Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation was required in p53-mediated neuronal cell death, caspase-3-deficient neurons were examined. Our results indicate that caspase-3-deficient neurons exhibit a remarkable delay in apoptosis and a dramatic decrease in TUNEL-positive cells. These studies demonstrate that p53-induced cell death in postmitotic neurons involves a Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation, suggesting that these molecules are important determinants in neuronal cell death after injury.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evidence for involvement of Bax and p53, but not caspases, in radiation-induced cell death of cultured postnatal hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci Res. 1998 Dec 15;54(6):721-33. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19981215)54:6<721::AID-JNR1>3.0.CO;2-1. J Neurosci Res. 1998. PMID: 9856857
-
Bcl-X(L)-caspase-9 interactions in the developing nervous system: evidence for multiple death pathways.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 1;21(1):169-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00169.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11150333 Free PMC article.
-
Injury-induced apoptosis of neurons in adult brain is mediated by p53-dependent and p53-independent pathways and requires Bax.J Comp Neurol. 2001 May 7;433(3):299-311. doi: 10.1002/cne.1141. J Comp Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11298357
-
p53-dependent apoptosis pathways.Adv Cancer Res. 2001;82:55-84. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(01)82002-9. Adv Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11447765 Review.
-
Cell death, Bcl-2, Bax, and the cerebellum.Cerebellum. 2002 Dec;1(4):277-87. doi: 10.1080/147342202320883588. Cerebellum. 2002. PMID: 12879966 Review.
Cited by
-
Bmi1 is down-regulated in the aging brain and displays antioxidant and protective activities in neurons.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031870. Epub 2012 Feb 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22384090 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Core Signaling Pathways of Hepatitis B Virus Pathogenesis for Biomarkers Identification and Drug Discovery via Systems Biology and Deep Learning Method.Biomedicines. 2020 Aug 31;8(9):320. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8090320. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32878239 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-mediated control of p53-associated cell death in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 7;26(23):6377-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0651-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16763046 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociating the dual roles of apoptosis-inducing factor in maintaining mitochondrial structure and apoptosis.EMBO J. 2006 Sep 6;25(17):4061-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601276. Epub 2006 Aug 17. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16917506 Free PMC article.
-
Morin ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity via targeting Nrf2/HO-1 and Bax/Bcl2/Caspase-3 signaling pathways.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3479-3488. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08286-8. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36781607
References
-
- Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1325. - PubMed
-
- Bacchetti S, Graham FL. Inhibition of cell proliferation by an adenovirus vector expressing the human wild-type p53 protein. Int J Oncol. 1993;3:781–788. - PubMed
-
- Banasiak KJ, Haddad GG. Hypoxia-induced apoptosis: effect of hypoxic severity and role of p53 in neuronal cell death. Brain Res. 1998;29:295–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
