Characterization of the inflammatory response to proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR2)-activating peptides in the rat paw
- PMID: 10455252
- PMCID: PMC1566112
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702634
Characterization of the inflammatory response to proteinase-activated receptor-2 (PAR2)-activating peptides in the rat paw
Abstract
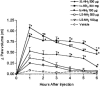
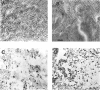
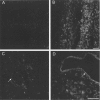
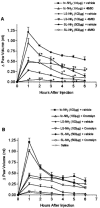
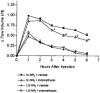
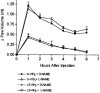
In the present study, we have observed the development of an inflammatory reaction in the rat hindpaw, following the injection of specific agonists of PAR2 (two PAR2 activating peptides). This inflammation was characterized by oedema and granulocyte infiltration. Two selective PAR2 activating peptides, SLGRL-NH2 and trans-cinnamoyl-LIGRLO-NH2 induced significant oedema in the rat hindpaw from 1-6 h following subplantar injection. Six hours after the PAR2-activating peptide injection, the paw tissues showed a complete disruption of tissue architecture along with an inflammatory cell infiltrate. In the inflamed paw, PAR2-immunoreactivity was expressed on endothelial cells as well as on the infiltrating inflammatory cells. The oedema induced by the injection of the two PAR2 activating peptides was slightly reduced in rats pre-treated with compound 48/80, but was not modified by pre-treatment of rats with cromolyn, a mast cell stabilizer. Pre-treatment of rats with a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor (indomethacin) or a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (L-N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester) had no effect on the oedema induced by the PAR2-activating peptides. These results demonstrate that the administration of PAR2-activating peptides into the rat paw induced an acute inflammatory response characterized by a persistent oedema (at least 6 h) and granulocyte infiltration. The PAR2-induced inflammatory response occurred through a mechanism largely independent of mast cell activation, and of the production of prostanoids and nitric oxide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pro- and anti-inflammatory actions of thrombin: a distinct role for proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1).Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Mar;126(5):1262-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702408. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10205017 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of vascular permeability by specific activation of protease-activated receptor-1 in rat hindpaw: a protective role of endogenous and exogenous nitric oxide.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Apr;126(8):1856-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702513. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10372830 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-2-activating peptides induce leukocyte rolling, adhesion, and extravasation in vivo.J Immunol. 1999 Nov 1;163(9):5064-9. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10528212
-
Proteinase-activated Receptor 2 (PAR2): a challenging new target for treatment of vascular diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(22):2769-78. doi: 10.2174/1381612043383656. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15320742 Review.
-
Tryptase and Exogenous Trypsin: Mechanisms and Ophthalmic Applications.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Mar 2;16:927-939. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S402900. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 36891173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protease-Activated Receptors (PARs): Biology and Therapeutic Potential in Perioperative Stroke.Transl Stroke Res. 2024 Feb 7. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01233-0. Online ahead of print. Transl Stroke Res. 2024. PMID: 38326662 Review.
-
Roles of protease-activated receptors in a mouse model of endotoxemia.Blood. 2006 May 15;107(10):3912-21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3130. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16434493 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that protease activated receptor 2 expression is enhanced in human coronary atherosclerotic lesions.J Clin Pathol. 2004 May;57(5):513-6. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2003.015156. J Clin Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15113859 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-1 agonists attenuate nociception in response to noxious stimuli.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;135(5):1101-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704568. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11877315 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of mouse protease-activated receptor-2 induces lymphocyte adhesion and generation of reactive oxygen species.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;149(5):591-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706905. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16981001 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AL-ANI B., SAIFEDDINE M., HOLLENBERG M.D. Detection of functional receptors for the proteinase-activated receptor-2-activating polypeptides, SLIGRL-NH2 in rat vascular and gastric smooth muscle. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1995;73:1203–1207. - PubMed
-
- DI ROSA M., GIROUD J.P., WILLOUGHBY D.A. Studies of the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats at different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J. Pathol. 1971;104:15–29. - PubMed
-
- EMILSSON K., WAHLESTEDT C., SUN M.K., NYSTEDT S., OWMAN C., SUNDELIN J. Vascular effects of proteinase-activated receptor 2 agonist peptide. J. Vasc. Res. 1997;34:267–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

