Tat-SF1 protein associates with RAP30 and human SPT5 proteins
- PMID: 10454543
- PMCID: PMC84462
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.9.5960
Tat-SF1 protein associates with RAP30 and human SPT5 proteins
Abstract
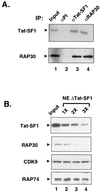
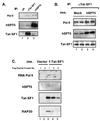
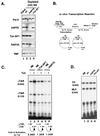
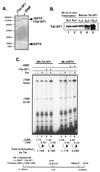
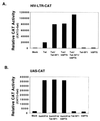
The potent transactivator Tat recognizes the transactivation response RNA element (TAR) of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and stimulates the processivity of elongation of RNA polymerase (Pol) II complexes. The cellular proteins Tat-SF1 and human SPT5 (hSPT5) are required for Tat activation as shown by immunodepletion with specific sera and complementation with recombinant proteins. In nuclear extracts, small fractions of both hSPT5 and Pol II are associated with Tat-SF1 protein. Surprisingly, the RAP30 protein of the heterodimeric transcription TFIIF factor is associated with Tat-SF1, while the RAP74 subunit of TFIIF is not coimmunoprecipitated with Tat-SF1. Overexpression of Tat-SF1 and hSPT5 specifically stimulates the transcriptional activity of Tat in vivo. These results suggest that Tat-SF1 and hSPT5 are indispensable cellular factors supporting Tat-specific transcription activation and that they may interact with RAP30 in controlling elongation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of the human homolog of the yeast transcription factor SPT5 in HIV-1 Tat-activation.J Mol Biol. 1998 Mar 27;277(2):179-97. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1601. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9514752
-
Modulating HIV-1 replication by RNA interference directed against human transcription elongation factor SPT5.Retrovirology. 2004 Dec 27;1:46. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-46. Retrovirology. 2004. PMID: 15620346 Free PMC article.
-
Spt5 cooperates with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat by preventing premature RNA release at terminator sequences.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;22(4):1079-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1079-1093.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11809800 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription elongation: the 'Foggy' is liftingellipsis.Curr Biol. 2001 Feb 20;11(4):R144-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00063-x. Curr Biol. 2001. PMID: 11250170 Review.
-
Tat, Tat-associated kinase, and transcription.J Biomed Sci. 1998;5(1):24-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02253352. J Biomed Sci. 1998. PMID: 9570510 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Elements Recognized by Abacavir-Induced T Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 7;18(7):1464. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071464. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28686208 Free PMC article.
-
Spt5 and spt6 are associated with active transcription and have characteristics of general elongation factors in D. melanogaster.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2623-34. doi: 10.1101/gad.831900. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040216 Free PMC article.
-
The pre-mRNA splicing and transcription factor Tat-SF1 is a functional partner of the spliceosome SF3b1 subunit via a U2AF homology motif interface.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 22;294(8):2892-2902. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006764. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30567737 Free PMC article.
-
Relief of two built-In autoinhibitory mechanisms in P-TEFb is required for assembly of a multicomponent transcription elongation complex at the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Aug;20(16):5897-907. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.16.5897-5907.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10913173 Free PMC article.
-
Tat-SF1 is not required for Tat transactivation but does regulate the relative levels of unspliced and spliced HIV-1 RNAs.PLoS One. 2009 May 27;4(5):e5710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005710. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19479034 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
