Analysis of the immunological responses to transferrin and lactoferrin receptor proteins from Moraxella catarrhalis
- PMID: 10417140
- PMCID: PMC96656
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.3793-3799.1999
Analysis of the immunological responses to transferrin and lactoferrin receptor proteins from Moraxella catarrhalis
Abstract
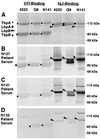
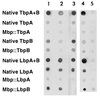
Moraxella catarrhalis expresses surface receptor proteins that specifically bind host transferrin (Tf) and lactoferrin (Lf) in the first step of the iron acquisition pathway. Acute- and convalescent-phase antisera from a series of patients with M. catarrhalis pulmonary infections were tested against Tf and Lf receptor proteins purified from the corresponding isolates. After the purified proteins had been separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting, we observed strong reactivity against Tf-binding protein B (TbpB; also called OMP1) and Lf-binding protein B (LbpB) but little or no reactivity against Tf-binding protein A (TbpA) or Lf-binding protein A (LbpA), using the convalescent-phase antisera. Considerable antigenic heterogeneity was observed when TbpBs and LbpBs isolated from different strains were tested with the convalescent-phase antisera. Comparison to the reactivity against electroblotted total cellular proteins revealed that the immune response against LbpB and TbpB constitutes a significant portion of the total detectable immune response to M. catarrhalis proteins. Preparations of affinity-isolated TbpA and LbpA reacted with convalescent-phase antisera in a solid-phase binding assay, but blocking with soluble TbpB, soluble LbpB, or extracts from an LbpA(-) mutant demonstrated that this reactivity was attributed to contaminants in the TbpA and LbpA preparations. These studies demonstrate the immunogenicity of M. catarrhalis TbpB and LbpB in humans and support their potential as vaccine candidates.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preparation and characterization of Neisseria meningitidis mutants deficient in production of the human lactoferrin-binding proteins LbpA and LbpB.J Bacteriol. 1998 Jun;180(12):3080-90. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3080-3090.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9620956 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and immunological properties of lactoferrin binding proteins from Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis.Microb Pathog. 1998 Feb;24(2):89-100. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1997.0173. Microb Pathog. 1998. PMID: 9480791
-
Cloning and expression of the Moraxella catarrhalis lactoferrin receptor genes.Infect Immun. 1998 Aug;66(8):3656-65. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.8.3656-3665.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9673246 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial lactoferrin receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;443:123-33. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-9068-9_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998. PMID: 9781351 Review.
-
Vaccines for Moraxella catarrhalis.Vaccine. 2000 Dec 8;19 Suppl 1:S101-7. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00287-5. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 11163472 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Moraxella catarrhalis CopB Protein in Facilitating Iron Acquisition From Human Transferrin and Lactoferrin.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 23;12:714815. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.714815. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34630348 Free PMC article.
-
Human immune response to outer membrane protein CD of Moraxella catarrhalis in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Infect Immun. 2003 Mar;71(3):1288-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1288-1294.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12595444 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive antigen screening identifies Moraxella catarrhalis proteins that induce protection in a mouse pulmonary clearance model.PLoS One. 2013 May 9;8(5):e64422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064422. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671716 Free PMC article.
-
A hag mutant of Moraxella catarrhalis strain O35E is deficient in hemagglutination, autoagglutination, and immunoglobulin D-binding activities.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4523-33. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4523-4533.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117964 Free PMC article.
-
The Moraxella catarrhalis porin-like outer membrane protein CD is an adhesin for human lung cells.Infect Immun. 2004 Apr;72(4):1906-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.4.1906-1913.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15039309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi C, Stone B, Beucher M, Cope L D, Maciver I, Thomas S E, McCracken G H, Jr, Sparling P F, Hansen E J. Expression of the CopB outer membrane protein by Moraxella catarrhalis is regulated by iron and affects iron acquisition from transferrin and lactoferrin. Infect Immun. 1996;64:2024–2030. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ala’Aldeen D A, Davies H A, Wall R A, Borriello S P. The 70 kilodalton iron regulated protein of Neisseria meningitidis is not the human transferrin receptor. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990;69:37–42. - PubMed
-
- Ala’Aldeen D A A, Borriello S P. The meningococcal transferrin-binding proteins 1 and 2 are both surface exposed and generate bactericidal antibodies capable of killing homologous and heterologous strains. Vaccine. 1996;14:49–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

