The CC-chemokine RANTES increases the attachment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to target cells via glycosaminoglycans and also activates a signal transduction pathway that enhances viral infectivity
- PMID: 10400729
- PMCID: PMC112716
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.8.6370-6379.1999
The CC-chemokine RANTES increases the attachment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to target cells via glycosaminoglycans and also activates a signal transduction pathway that enhances viral infectivity
Abstract
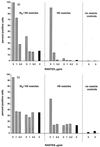
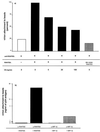
We have studied the mechanisms by which the CC-chemokine RANTES can enhance the infectivities of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and other enveloped viruses, when present at concentrations in excess of 500 ng/ml in vitro. Understanding the underlying mechanisms might throw light on fundamental processes of viral infection, in particular for HIV-1. Our principal findings are twofold: firstly, that oligomers of RANTES can cross-link enveloped viruses, including HIV-1, to cells via glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) present on the membranes of both virions and cells; secondly, that oligomers of RANTES interact with cell-surface GAGs to transduce a herbimycin A-sensitive signal which, over a period of several hours, renders the cells more permissive to infection by several viruses, including HIV-1. The enhancement mechanisms require that RANTES oligomerize either in solution or following binding to GAGs, since no viral infectivity enhancement is observed with a mutant form of the RANTES molecule that contains a single-amino-acid change (glutamic acid to serine at position 66) which abrogates oligomerization.
Figures
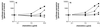

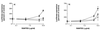
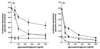
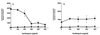
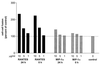
Similar articles
-
Interaction of the CC-chemokine RANTES with glycosaminoglycans activates a p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent signaling pathway and enhances human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2245-54. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2245-2254.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836402 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection by the CC-chemokine RANTES is independent of the mechanism of virus-cell fusion.J Virol. 1999 Jan;73(1):684-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.684-694.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9847374 Free PMC article.
-
Envelope-dependent, cyclophilin-independent effects of glycosaminoglycans on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 attachment and infection.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(12):6332-43. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.6332-6343.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12021366 Free PMC article.
-
The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1.Nature. 1996 Aug 29;382(6594):833-5. doi: 10.1038/382833a0. Nature. 1996. PMID: 8752281
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 and chemokines: beyond competition for common cellular receptors.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001 Jun-Sep;12(2-3):219-43. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(00)00033-2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001. PMID: 11325604 Review.
Cited by
-
Virus-Induced Cell Fusion and Syncytia Formation.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024;71:283-318. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-37936-9_14. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024. PMID: 37996683
-
The human herpesvirus 6 G protein-coupled receptor homolog U51 positively regulates virus replication and enhances cell-cell fusion in vitro.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):11914-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11914-11924.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16140767 Free PMC article.
-
Hemofiltrate CC chemokine 1[9-74] causes effective internalization of CCR5 and is a potent inhibitor of R5-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains in primary T cells and macrophages.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Apr;46(4):982-90. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.4.982-990.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11897579 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of chemokines by human fetal microglia after treatment with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein Tat.J Neurovirol. 2004 Apr;10(2):86-97. doi: 10.1080/13550280490279807. J Neurovirol. 2004. PMID: 15204927
-
Peptide and protein-based inhibitors of HIV-1 co-receptors.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 May;238(5):442-9. doi: 10.1177/1535370213480696. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 23856897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Amara A, Le Gall S, Schwartz O, Salamero J, Montes M, Loetscher P, Baggiolini M, Virelizier J-L, Arenzana-Seisdedos F. HIV coreceptor downregulation as antiviral principle: SDF-1α-dependent internalization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 contributes to inhibition of HIV replication. J Exp Med. 1997;186:139–146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amzazi S, Ylisastigul Y L, Bakri Y, Rabehi L, Gattegno L, Parmentier M, Gluckman J C, Benjouad A. The inhibitory effect of RANTES on the infection of primary macrophages by R5 human immunodeficiency virus type-1 depends on the macrophage activation state. Virology. 1998;252:96–105. - PubMed
-
- Arenzana-Seisedos F, Virelizier J-L, Rousset D, Clark-Lewis I, Loetscher P, Moser B, Baggiolini M. HIV blocked by chemokine antagonist. Nature. 1996;383:400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

