Trimeric association of Hox and TALE homeodomain proteins mediates Hoxb2 hindbrain enhancer activity
- PMID: 10373562
- PMCID: PMC84356
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.7.5134
Trimeric association of Hox and TALE homeodomain proteins mediates Hoxb2 hindbrain enhancer activity
Abstract
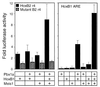
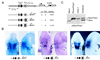
Pbx/exd proteins modulate the DNA binding affinities and specificities of Hox proteins and contribute to the execution of Hox-dependent developmental programs in arthropods and vertebrates. Pbx proteins also stably heterodimerize and bind DNA with Meis and Pknox1-Prep1, additional members of the TALE (three-amino-acid loop extension) superclass of homeodomain proteins that function on common genetic pathways with a subset of Hox proteins. In this study, we demonstrated that Pbx and Meis bind DNA as heterotrimeric complexes with Hoxb1 on a genetically defined Hoxb2 enhancer, r4, that mediates the cross-regulatory transcriptional effects of Hoxb1 in vivo. The DNA binding specificity of the heterotrimeric complex for r4 is mediated by a Pbx-Hox site in conjunction with a distal Meis site, which we showed to be required for ternary complex formation and Meis-enhanced transcription. Formation of heterotrimeric complexes in which all three homeodomains bind their cognate DNA sites is topologically facilitated by the ability of Pbx and Meis to interact through their amino termini and bind DNA without stringent half-site orientation and spacing requirements. Furthermore, Meis site mutation in the Hoxb2 enhancer phenocopies Pbx-Hox site mutation to abrogate enhancer-directed expression of a reporter transgene in the murine embryonic hindbrain, demonstrating that DNA binding by all three proteins is required for trimer function in vivo. Our data provide in vitro and in vivo evidence for the combinatorial regulation of Hox and TALE protein functions that are mediated, in part, by their interdependent DNA binding activities as ternary complexes. As a consequence, Hoxb1 employs Pbx and Meis-related proteins, as a pair of essential cofactors in a higher-order molecular complex, to mediate its transcriptional effects on an endogenous Hox response element.
Figures
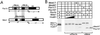

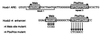



Similar articles
-
Segmental expression of Hoxb2 in r4 requires two separate sites that integrate cooperative interactions between Prep1, Pbx and Hox proteins.Development. 2000 Jan;127(1):155-66. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.1.155. Development. 2000. PMID: 10654609
-
A conserved motif N-terminal to the DNA-binding domains of myogenic bHLH transcription factors mediates cooperative DNA binding with pbx-Meis1/Prep1.Nucleic Acids Res. 1999 Sep 15;27(18):3752-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.18.3752. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999. PMID: 10471746 Free PMC article.
-
PBX and MEIS as non-DNA-binding partners in trimeric complexes with HOX proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7577-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7577. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523646 Free PMC article.
-
Hox cofactors in vertebrate development.Dev Biol. 2006 Mar 15;291(2):193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.032. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16515781 Review.
-
Biochemistry of the tale transcription factors PREP, MEIS, and PBX in vertebrates.Dev Dyn. 2014 Jan;243(1):59-75. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24016. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 23873833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hox regulation of transcription: more complex(es).Dev Dyn. 2014 Jan;243(1):4-15. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23997. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 23765878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p160 Myb-binding protein interacts with Prep1 and inhibits its transcriptional activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(22):7981-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01290-07. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17875935 Free PMC article.
-
p21 is a transcriptional target of HOXA10 in differentiating myelomonocytic cells.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2581-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.817100. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040212 Free PMC article.
-
Prep1 (pKnox1)-deficiency leads to spontaneous tumor development in mice and accelerates EmuMyc lymphomagenesis: a tumor suppressor role for Prep1.Mol Oncol. 2010 Apr;4(2):126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 7. Mol Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20106730 Free PMC article.
-
Pbx1/Pbx2 govern axial skeletal development by controlling Polycomb and Hox in mesoderm and Pax1/Pax9 in sclerotome.Dev Biol. 2008 Sep 15;321(2):500-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.04.005. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18691704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aspland S E, White R A H. Nucleocytoplasmic localisation of extradenticle protein is spatially regulated throughout development in Drosophila. Development. 1997;124:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Bischof L J, Kagawa N, Moskow J J, Takahashi Y, Iwamatsu A, Buchberg A M, Waterman M R. Members of the meis1 and pbx homeodomain protein families cooperatively bind a cAMP-responsive sequence (CRS1) from bovine CYP17. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:7941–7948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
