Gibberellin dose-response curves and the characterization of dwarf mutants of barley
- PMID: 10364415
- PMCID: PMC59302
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.120.2.623
Gibberellin dose-response curves and the characterization of dwarf mutants of barley
Abstract
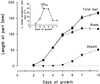
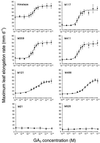
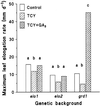
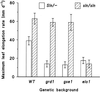
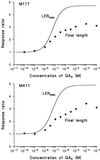
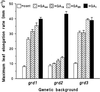
Dose-response curves relating gibberellin (GA) concentration to the maximal leaf-elongation rate (LERmax) defined three classes of recessive dwarf mutants in the barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) 'Himalaya. ' The first class responded to low (10(-8)-10(-6) M) [GA3] (as did the wild type). These grd (GA-responsive dwarf) mutants are likely to be GA-biosynthesis mutants. The second class of mutant, gse (GA sensitivity), differed principally in GA sensitivity, requiring approximately 100-fold higher [GA3] for both leaf elongation and alpha-amylase production by aleurone. This novel class may have impaired recognition between the components that are involved in GA signaling. The third class of mutant showed no effect of GA3 on the LERmax. When further dwarfed by treatment with a GA-biosynthesis inhibitor, mutants in this class did respond to GA3, although the LERmax never exceeded that of the untreated dwarf. These mutants, called elo (elongation), appeared to be defective in the specific processes that are required for elongation rather than in GA signaling. When sln1 (slender1) was introduced into these different genetic backgrounds, sln was epistatic to grd and gse but hypostatic to elo. Because the rapid leaf elongation typical of sln was observed in the grd and gse backgrounds, we inferred that rapid leaf elongation is the default state and suggest that GA action is mediated through the activity of the product of the Sln gene.
Figures
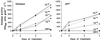
Similar articles
-
Mutants at the Slender1 locus of barley cv Himalaya. Molecular and physiological characterization.Plant Physiol. 2002 May;129(1):181-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.010917. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12011349 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of gibberellin-insensitive mutants selected from among dwarf mutants of rice.Theor Appl Genet. 1994 Jan;87(6):705-12. doi: 10.1007/BF00222896. Theor Appl Genet. 1994. PMID: 24190414
-
Gibberellin signaling in barley aleurone cells. Control of SLN1 and GAMYB expression.Plant Physiol. 2002 May;129(1):191-200. doi: 10.1104/pp.010918. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12011350 Free PMC article.
-
Slender barley: A constitutive gibberellin-response mutant.Planta. 1988 Jul;175(1):107-14. doi: 10.1007/BF00402887. Planta. 1988. PMID: 24221634
-
'Overgrowth' mutants in barley and wheat: new alleles and phenotypes of the 'Green Revolution' DELLA gene.J Exp Bot. 2013 Apr;64(6):1603-13. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert022. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23382550 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gibberellin signaling: biosynthesis, catabolism, and response pathways.Plant Cell. 2002;14 Suppl(Suppl):S61-80. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010476. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12045270 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The CYP88A cytochrome P450, ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase, catalyzes three steps of the gibberellin biosynthesis pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 13;98(4):2065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.2065. Epub 2001 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11172076 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function mutation of the Rapid Alkalinization Factor (RALF1)-like peptide in the dandelion Taraxacum koksaghyz entails a high-biomass taproot phenotype.PLoS One. 2019 May 24;14(5):e0217454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217454. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31125376 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a null allelic mutant of the rice NAL1 gene reveals its role in regulating cell division.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0118169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118169. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658704 Free PMC article.
-
Gibberellin-induced changes in growth anisotropy precede gibberellin-dependent changes in cortical microtubule orientation in developing epidermal cells of barley leaves. Kinematic and cytological studies on a gibberellin-responsive dwarf mutant, M489.Plant Physiol. 2000 Oct;124(2):813-22. doi: 10.1104/pp.124.2.813. Plant Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11027729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- A'Brook R (1987) PEST User Guide Vols 10 and 11, Plant Hormone Versions
-
- Boother GM, Gale MD, Gaskin P, MacMillan J, Sponsel VM . Gibberellins in shoots of Hordeum vulgare: a comparison between cv. Triumph and two dwarf mutants which differ in their response to gibberellin. Physiol Plant. 1991;81:385–392.
-
- Chandler PM. Hormonal regulation of gene expression in the “slender” mutant of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Planta. 1988;175:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Chandler PM, Jacobsen JV. Primer extension studies on α-amylase mRNAs in barley aleurone. II. Hormonal regulation of expression. Plant Mol Biol. 1991;16:637–645. - PubMed
-
- Clouse SD, Sasse JM. Brassinosteroids: essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1998;49:427–451. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

