PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light
- PMID: 10357859
- PMCID: PMC98974
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.63.2.479-506.1999
PAS domains: internal sensors of oxygen, redox potential, and light
Abstract
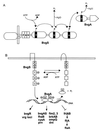
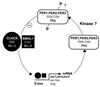
PAS domains are newly recognized signaling domains that are widely distributed in proteins from members of the Archaea and Bacteria and from fungi, plants, insects, and vertebrates. They function as input modules in proteins that sense oxygen, redox potential, light, and some other stimuli. Specificity in sensing arises, in part, from different cofactors that may be associated with the PAS fold. Transduction of redox signals may be a common mechanistic theme in many different PAS domains. PAS proteins are always located intracellularly but may monitor the external as well as the internal environment. One way in which prokaryotic PAS proteins sense the environment is by detecting changes in the electron transport system. This serves as an early warning system for any reduction in cellular energy levels. Human PAS proteins include hypoxia-inducible factors and voltage-sensitive ion channels; other PAS proteins are integral components of circadian clocks. Although PAS domains were only recently identified, the signaling functions with which they are associated have long been recognized as fundamental properties of living cells.
Figures



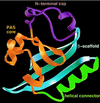


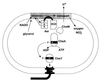
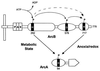




Similar articles
-
Structural basis for PAS domain heterodimerization in the basic helix--loop--helix-PAS transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Dec 23;100(26):15504-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2533374100. Epub 2003 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14668441 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the murine Hif-1 alpha locus.Gene Expr. 1997;6(5):287-99. Gene Expr. 1997. PMID: 9368100 Free PMC article.
-
Prokaryotic homologs of the eukaryotic DNA-end-binding protein Ku, novel domains in the Ku protein and prediction of a prokaryotic double-strand break repair system.Genome Res. 2001 Aug;11(8):1365-74. doi: 10.1101/gr.181001. Genome Res. 2001. PMID: 11483577 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of Per-ARNT-Sim domains and their possible role in the life-cycle biology of Trypanosoma cruzi.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018 Jan;219:52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 11. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29133150 Review.
-
The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;36(2):189-204. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(03)00211-5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14643885 Review.
Cited by
-
PAS domains in bacterial signal transduction.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021 Jun;61:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33647528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling mechanisms of LOV domains: new insights from molecular dynamics studies.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2013 Jul;12(7):1158-70. doi: 10.1039/c3pp25400c. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23407663 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse effects of adaptive mutation to survive static culture conditions on successful fitness of the rice pathogen Burkholderia glumae in a host.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 24;15(8):e0238151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238151. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32833990 Free PMC article.
-
A Model of the Full-Length Cytokinin Receptor: New Insights and Prospects.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 20;25(1):73. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010073. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203244 Free PMC article.
-
LOV domain-containing F-box proteins: light-dependent protein degradation modules in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant. 2012 May;5(3):573-82. doi: 10.1093/mp/sss013. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Plant. 2012. PMID: 22402262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad M, Jarillo J A, Smirnova O, Cashmore A R. The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol Cell. 1998;1:939–948. - PubMed
-
- Akerley B J, Miller J F. Understanding signal transduction during bacterial infection. Trends Microbiol. 1996;4:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Alex L A, Simon M I. Protein histidine kinases and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1994;10:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Allada R, White N E, So W V, Hall J C, Rosbash M. A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell. 1998;93:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

