Bax, but not Bcl-xL, decreases the lifetime of planar phospholipid bilayer membranes at subnanomolar concentrations
- PMID: 10318911
- PMCID: PMC21887
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5492
Bax, but not Bcl-xL, decreases the lifetime of planar phospholipid bilayer membranes at subnanomolar concentrations
Abstract
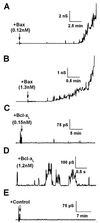
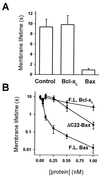
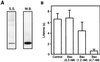
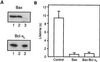
Release of proteins through the outer mitochondrial membrane can be a critical step in apoptosis, and the localization of apoptosis-regulating Bcl-2 family members there suggests they control this process. We used planar phospholipid membranes to test the effect of full-length Bax and Bcl-xL synthesized in vitro and native Bax purified from bovine thymocytes. Instead of forming pores with reproducible conductance levels expected for ionic channels, Bax, but not Bcl-xL, created arbitrary and continuously variable changes in membrane permeability and decreased the stability of the membrane, regardless of whether the source of the protein was synthetic or native. This breakdown of the membrane permeability barrier and destabilization of the bilayer was quantified by using membrane lifetime measurements. Bax decreased membrane lifetime in a voltage- and concentration-dependent manner. Bcl-xL did not protect against Bax-induced membrane destabilization, supporting the idea that these two proteins function independently. Corresponding to a physical theory for lipidic pore formation, Bax potently diminished the linear tension of the membrane (i.e., the energy required to form the edge of a new pore). We suggest that Bax acts directly by destabilizing the lipid bilayer structure of the outer mitochondrial membrane, promoting the formation of a pore-the apoptotic pore-large enough to allow mitochondrial proteins such as cytochrome c to be released into the cytosol. Bax could then enter and permeabilize the inner mitochondrial membrane through the same hole.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of bax-induced release of cytochrome c from yeast mitochondria permeability of mitochondrial membranes, role of VDAC and ATP requirement.Eur J Biochem. 1999 Mar;260(3):684-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00198.x. Eur J Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10102996
-
Bid acts on the permeability transition pore complex to induce apoptosis.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 14;19(54):6342-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204030. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11175349
-
Integration and oligomerization of Bax protein in lipid bilayers characterized by single molecule fluorescence study.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 14;289(46):31708-31718. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.583393. Epub 2014 Oct 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25288797 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation by Bax/Bak.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 May 9;304(3):455-61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00617-x. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12729579 Review.
-
Regulation of Bax mitochondrial localization by Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L): keep your friends close but your enemies closer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;45(1):64-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.09.022. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23064052 Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency of the Bax gene attenuates denervation-induced apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2006 Jun;11(6):967-81. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-6315-4. Apoptosis. 2006. PMID: 16763784 Free PMC article.
-
Helix orientations in membrane-associated Bcl-X(L) determined by 15N-solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Eur Biophys J. 2007 Dec;37(1):71-80. doi: 10.1007/s00249-007-0165-z. Epub 2007 May 10. Eur Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17492281
-
Role of oxidative phosphorylation in Bax toxicity.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 May;20(10):3590-6. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.10.3590-3596.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10779348 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics.Dev Cell. 2011 Jul 19;21(1):92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.017. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 21763611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen peroxide-induced Akt phosphorylation regulates Bax activation.Biochimie. 2009 May;91(5):577-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.01.010. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 19278624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muchmore S W, Sattler M, Liang H, Meadows R P, Harlan J E, Yoon H S, Nettesheim D, Chang B S, Thompson C B, Wong S L, et al. Nature (London) 1996;381:335–341. - PubMed
-
- Minn J A, Velez P, Schendel S L, Liang H, Muchmore S W, Fesik S W, Fill M, Thompson C B. Nature (London) 1997;385:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta A, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod J J, Mazzei G, et al. Science. 1997;277:370–372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

