In vivo replication of recombinant murine cytomegalovirus driven by the paralogous major immediate-early promoter-enhancer of human cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 10233967
- PMCID: PMC112549
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.5043-5055.1999
In vivo replication of recombinant murine cytomegalovirus driven by the paralogous major immediate-early promoter-enhancer of human cytomegalovirus
Abstract
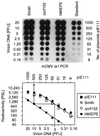
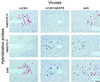
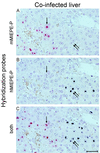
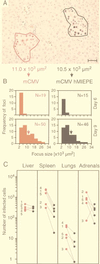
Transcription of the major immediate-early (MIE) genes of cytomegaloviruses (CMV) is driven by a strong promoter-enhancer (MIEPE) complex. Transactivator proteins encoded by these MIE genes are essential for productive infection. Accordingly, the MIEPE is a crucial control point, and its regulation by activators and repressors is pertinent to virus replication. Since the MIEPE contains multiple regulatory elements, it was reasonable to assume that specific sequence motifs are irreplaceable for specifying the cell-type tropism and replication pattern. Recent work on murine CMV infectivity (A. Angulo, M. Messerle, U. H. Koszinowski, and P. Ghazal, J. Virol. 72:8502-8509, 1998) has documented the proposed enhancing function of the enhancer in that its resection or its replacement by a nonregulatory stuffer sequence resulted in a significant reduction of infectivity, even though replication competence was maintained by a basal activity of the spared authentic MIE promoter. Notably, full capacity for productive in vitro infection of fibroblasts was restored in recombinant viruses by the human CMV enhancer. Using two-color in situ hybridization with MIEPE-specific polynucleotide probes, we demonstrated that a murine CMV recombinant in which the complete murine CMV MIEPE is replaced by the paralogous human CMV core promoter and enhancer (recombinant virus mCMVhMIEPE) retained the potential to replicate in vivo in all tissues relevant to CMV disease. Notably, mCMVhMIEPE was also found to replicate in the liver, a site at which transgenic hCMV MIEPE is silenced. We conclude that productive in vivo infection with murine CMV does not strictly depend on a MIEPE type-specific regulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rat cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer switching results in altered growth characteristics.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(11):5076-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5076-5083.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11333888 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early enhancer determines the efficiency of immediate-early gene transcription and viral replication in permissive cells at low multiplicity of infection.J Virol. 2003 Mar;77(6):3602-14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.6.3602-3614.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12610136 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular homeoproteins, SATB1 and CDP, bind to the unique region between the human cytomegalovirus UL127 and major immediate-early genes.Virology. 2007 Sep 15;366(1):117-25. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.04.024. Epub 2007 May 18. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17512569
-
Role of the proximal enhancer of the major immediate-early promoter in human cytomegalovirus replication.J Virol. 2004 Dec;78(23):12788-99. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.23.12788-12799.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15542631 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the cytomegalovirus major immediate early enhancer in acute infection and reactivation from latency.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):223-31. doi: 10.1007/s00430-007-0069-7. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18097687 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive Role of the MHC Class-I Antigen Presentation Regulator m04/gp34 of Murine Cytomegalovirus in Antiviral Protection by CD8 T Cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 26;10:454. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00454. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32984075 Free PMC article.
-
Bile Acids Act as Soluble Host Restriction Factors Limiting Cytomegalovirus Replication in Hepatocytes.J Virol. 2016 Jul 11;90(15):6686-6698. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00299-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27170759 Free PMC article.
-
Transactivation of cellular genes involved in nucleotide metabolism by the regulatory IE1 protein of murine cytomegalovirus is not critical for viral replicative fitness in quiescent cells and host tissues.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(20):9900-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00928-08. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18684825 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of multiple cis-acting elements in the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early distal enhancer for viral gene expression and replication.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(1):313-26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.1.313-326.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11739696 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early regulatory region and viral replication in embryonal NTera2 cells: role of trichostatin A, retinoic acid, and deletion of the 21-base-pair repeats and modulator.J Virol. 2001 Feb;75(4):1581-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.4.1581-1593.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angulo A, Suto C, Heyman R A, Ghazal P. Characterization of the sequences of the human cytomegalovirus enhancer that mediate differential regulation by natural and synthetic retinoids. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10:781–793. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

