Coiled bodies preferentially associate with U4, U11, and U12 small nuclear RNA genes in interphase HeLa cells but not with U6 and U7 genes
- PMID: 10233169
- PMCID: PMC30488
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1653
Coiled bodies preferentially associate with U4, U11, and U12 small nuclear RNA genes in interphase HeLa cells but not with U6 and U7 genes
Abstract
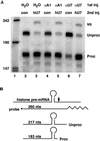
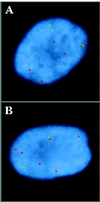
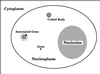
Coiled bodies (CBs) are nuclear organelles involved in the metabolism of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and histone messages. Their structural morphology and molecular composition have been conserved from plants to animals. CBs preferentially and specifically associate with genes that encode U1, U2, and U3 snRNAs as well as the cell cycle-regulated histone loci. A common link among these previously identified CB-associated genes is that they are either clustered or tandemly repeated in the human genome. In an effort to identify additional loci that associate with CBs, we have isolated and mapped the chromosomal locations of genomic clones corresponding to bona fide U4, U6, U7, U11, and U12 snRNA loci. Unlike the clustered U1 and U2 genes, each of these loci encode a single gene, with the exception of the U4 clone, which contains two genes. We next examined the association of these snRNA genes with CBs and found that they colocalized less frequently than their multicopy counterparts. To differentiate a lower level of preferential association from random colocalization, we developed a theoretical model of random colocalization, which yielded expected values for chi2 tests against the experimental data. Certain single-copy snRNA genes (U4, U11, and U12) but not controls were found to significantly (p < 0.000001) associate with CBs. Recent evidence indicates that the interactions between CBs and genes are mediated by nascent transcripts. Taken together, these new results suggest that CB association may be substantially augmented by the increased transcriptional capacity of clustered genes. Possible functional roles for the observed interactions of CBs with snRNA genes are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coiled bodies contain U7 small nuclear RNA and associate with specific DNA sequences in interphase human cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):5915-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.5915. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7597053 Free PMC article.
-
Human genes encoding U3 snRNA associate with coiled bodies in interphase cells and are clustered on chromosome 17p11.2 in a complex inverted repeat structure.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Dec 1;25(23):4740-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.23.4740. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9365252 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-mediated interaction of Cajal bodies and U2 snRNA genes.J Cell Biol. 2001 Aug 6;154(3):499-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105084. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11489914 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoplasmic organization of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in cultured human cells.J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(4):715-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.4.715. J Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8491767 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of transcription enforces the formation of distinct nuclear bodies in zebrafish embryos.RNA Biol. 2017 Jun 3;14(6):752-760. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1255397. Epub 2016 Nov 18. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27858508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear body movement is determined by chromatin accessibility and dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 7;101(36):13221-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402958101. Epub 2004 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15331777 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of splicing proteins and putative coiled bodies during pollen development and androgenesis in Brassica napus L.Protoplasma. 2001;216(3-4):191-200. doi: 10.1007/BF02673871. Protoplasma. 2001. PMID: 11732187
-
Genetic analysis of nuclear bodies: from nondeterministic chaos to deterministic order.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:365-74. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.043. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21467138 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral imaging to visualize higher-order genomic organization.Nucleus. 2016 May 3;7(3):325-38. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1187344. Epub 2016 May 11. Nucleus. 2016. PMID: 27167405 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of cell nucleus organisation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jul;3(7):e138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030138. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17676980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anisari-Lari MA, Shen Y, Muzny DM, Lee W, Gibbs RA. Large-scale sequencing in human chromosome 12p13: experimental and computational gene structure determination. Genome Res. 1997;7:268–280. - PubMed
-
- Ballard SG, Ward DC. Fluorescence in situ hybridization using digital imaging microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41:1755–1759. - PubMed
-
- Bark C, Weller P, Zabielski J, Pettersson U. Genes for human U4 small nuclear RNA. Gene. 1986;50:333–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

