Two roads diverged: interferon alpha/beta- and interleukin 12-mediated pathways in promoting T cell interferon gamma responses during viral infection
- PMID: 10209048
- PMCID: PMC2193028
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.8.1315
Two roads diverged: interferon alpha/beta- and interleukin 12-mediated pathways in promoting T cell interferon gamma responses during viral infection
Abstract
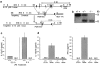
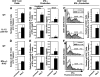
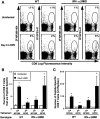
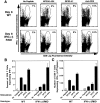
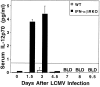
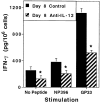
Viral infections induce CD8 T cell expansion and interferon (IFN)-gamma production for defense, but the innate cytokines shaping these responses have not been identified. Although interleukin (IL)-12 has the potential to contribute, IL-12-dependent T cell IFN-gamma has not been detected during viral infections. Moreover, certain viruses fail to induce IL-12, and elicit high levels of IFN-alpha/beta to negatively regulate it. The endogenous factors promoting virus-induced T cell IFN-gamma production were defined in studies evaluating CD8 T cell responses during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infections of mice. Two divergent supporting pathways were characterized. Under normal conditions of infections, the CD8 T cell IFN-gamma response was dependent on endogenous IFN-alpha/beta effects, but was IL-12 independent. In contrast, in the absence of IFN-alpha/beta functions, an IL-12 response was revealed and substituted an alternative pathway to IFN-gamma. IFN-alpha/beta-mediated effects resulted in enhanced, but the alternative pathway also promoted, resistance to infection. These observations define uniquely important IFN-alpha/beta-controlled pathways shaping T cell responses during viral infections, and demonstrate plasticity of immune responses in accessing divergent innate mechanisms to achieve similar ultimate goals.
Figures

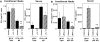
Similar articles
-
Interferon alpha/beta and interleukin 12 responses to viral infections: pathways regulating dendritic cell cytokine expression in vivo.J Exp Med. 2002 Feb 18;195(4):517-28. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011672. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 11854364 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cells in innate immune responses: using STAT4-dependent but antigen-independent pathways to gamma interferon during viral infection.mBio. 2014 Oct 21;5(5):e01978-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01978-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25336459 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role for alpha/beta and gamma interferons in persistence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus by clonal exhaustion of cytotoxic T cells.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8407-23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8407-8423.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507186 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Il-12 and Type I Interferon in Governing the Magnitude of CD8 T Cell Responses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;850:31-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-15774-0_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26324344 Review.
-
Confounding roles for type I interferons during bacterial and viral pathogenesis.Int Immunol. 2013 Dec;25(12):663-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt050. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Int Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24158954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
West Nile virus-infected human dendritic cells fail to fully activate invariant natural killer T cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Nov;186(2):214-226. doi: 10.1111/cei.12850. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27513522 Free PMC article.
-
Human macrophages, but not dendritic cells, are activated and produce alpha/beta interferons in response to Mopeia virus infection.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(19):10516-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.19.10516-10524.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15367618 Free PMC article.
-
Role of interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-12, and gamma interferon in primary and vaccine-primed immune responses to Friend retrovirus infection.J Virol. 2001 Jan;75(2):654-60. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.2.654-660.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11134279 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated alpha interferon is an effective treatment for virulent venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and has profound effects on the host immune response to infection.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(11):5006-15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.5006-5015.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10799574 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolate in mice is determined by failure to induce Th1 type immunity and is associated with induction of IFN-alpha /beta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 May 8;98(10):5752-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091096998. Epub 2001 Apr 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11320211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biron CA, Gazzinelli RT. Effects of IL-12 on immune responses to microbial infections: a key mediator in regulating disease outcome. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:485–496. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA. Innate immunity: impact on the adaptive immune response. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh C-S, Macetionia SE, Tripp CS, Wolf SF, O'Garra A, Murphy KM. Development of Th1 CD4+ T cells through IL-12 produced by Listeria-induced macrophages. Science. 1993;260:547–549. - PubMed
-
- Manetti R, Parronchi P, Giudizi MG, Piccinni MP, Maggi E, Trinchieri G, Romagnani S. Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (interleukin 12 [IL-12]) induces T helper type 1 (Th1)–specific immune responses and inhibits the development of IL-4-producing Th cells. J Exp Med. 1993;177:1199–1204. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

