The transmembrane sequence of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-C as a determinant in inhibition of a subset of natural killer cells
- PMID: 10209043
- PMCID: PMC2193022
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.8.1265
The transmembrane sequence of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-C as a determinant in inhibition of a subset of natural killer cells
Abstract
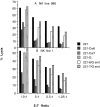
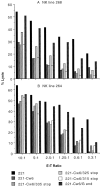
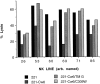
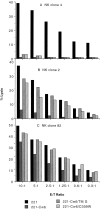
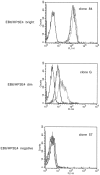
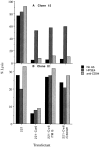
Molecular interactions with the extracellular domains of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins are major determinants of immune recognition that have been extensively studied both physically and biochemically. However, no immunological function has yet been placed on the transmembrane or cytoplasmic amino acid sequences of these proteins despite strict conservation of unique features within each class I major histocompatibility complex locus. Here we report that lysis by a subset of natural killer (NK) cells inhibited by target cell expression of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-Cw6 or -Cw7 was not inhibited by expression of chimeric proteins consisting of the extracellular domains of HLA-C and the COOH-terminal portion of HLA-G. Assays using transfectants expressing a variety of HLA-Cw6 mutants identified the transmembrane sequence and, in particular, cysteine at position 309 as necessary for inhibition of 68% (25/37) of NK cell lines and 23% (33/145) of NK clones tested. Moreover, these NK clones inhibited by target cell expression of HLA-Cw6 and dependent upon the transmembrane sequence were found not to express or to only dimly express NK inhibitory receptors (NKIR1) that are EB6/HP3E4-positive. Furthermore, assays using monoclonal antibody blocking suggest that an NK receptor other than NKIR1 or CD94 is responsible for recognition dependent upon the transmembrane sequence of HLA-Cw6.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recognition of HLA-Cw4 but not HLA-Cw6 by the NK cell receptor killer cell Ig-like receptor two-domain short tail number 4.J Immunol. 2001 Jun 15;166(12):7260-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.12.7260. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11390475
-
Human T cell receptor-mediated recognition of HLA-E.Eur J Immunol. 2002 Apr;32(4):936-44. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200204)32:4<936::AID-IMMU936>3.0.CO;2-M. Eur J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11920559
-
A human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-G-specific receptor expressed on all natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 5;189(7):1093-100. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1093. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10190900 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell recognition of HLA class I molecules.Rev Immunogenet. 2000;2(3):433-48. Rev Immunogenet. 2000. PMID: 11256749 Review.
-
Human uterine lymphocytes.Hum Reprod Update. 1998 Sep-Oct;4(5):480-5. doi: 10.1093/humupd/4.5.480. Hum Reprod Update. 1998. PMID: 10027599 Review.
Cited by
-
Intercellular transfer and supramolecular organization of human leukocyte antigen C at inhibitory natural killer cell immune synapses.J Exp Med. 2001 Nov 19;194(10):1507-17. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.10.1507. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11714757 Free PMC article.
-
The multi-faceted nature of HLA class I dimer molecules.Immunology. 2012 Aug;136(4):380-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03593.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22533699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fifty years of HLA-associated type 1 diabetes risk: history, current knowledge, and future directions.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1457213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457213. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39328411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human natural killer cell immune synapse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 21;96(26):15062-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15062. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10611338 Free PMC article.
-
Injection of pre-psoriatic skin with CD4+ T cells induces psoriasis.Am J Pathol. 1999 Jul;155(1):145-58. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65109-7. Am J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10393847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ljunggren H-G, Karre K. In search of the missing self: MHC molecules and NK recognition. Immunol Today. 1990;11:7–10. - PubMed
-
- Karre K. How to recognise a foreign submarine. Immunol Rev. 1997;155:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Colonna M, Samaridis J. Cloning of immunoglobulin superfamily members associated with HLA-C allele and HLA-B recognition by human natural killer cells. Science. 1995;268:405–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

