Automated MAD and MIR structure solution
- PMID: 10089316
- PMCID: PMC2746121
- DOI: 10.1107/s0907444999000839
Automated MAD and MIR structure solution
Abstract
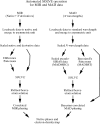
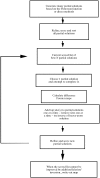
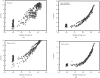
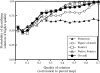
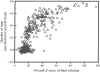
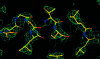
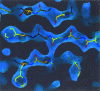
Obtaining an electron-density map from X-ray diffraction data can be difficult and time-consuming even after the data have been collected, largely because MIR and MAD structure determinations currently require many subjective evaluations of the qualities of trial heavy-atom partial structures before a correct heavy-atom solution is obtained. A set of criteria for evaluating the quality of heavy-atom partial solutions in macromolecular crystallography have been developed. These have allowed the conversion of the crystal structure-solution process into an optimization problem and have allowed its automation. The SOLVE software has been used to solve MAD data sets with as many as 52 selenium sites in the asymmetric unit. The automated structure-solution process developed is a major step towards the fully automated structure-determination, model-building and refinement procedure which is needed for genomic scale structure determinations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Automated structure solution, density modification and model building.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002 Nov;58(Pt 11):1937-40. doi: 10.1107/s0907444902016438. Epub 2002 Oct 21. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002. PMID: 12393925
-
Automated structure solution with the PHENIX suite.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;426:419-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-058-8_28. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18542881
-
A highly automated heavy-atom search procedure for macromolecular structures.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1999 Sep;55(Pt 9):1568-77. doi: 10.1107/s0907444999007763. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 1999. PMID: 10489451 Review.
-
SOLVE and RESOLVE: automated structure solution, density modification and model building.J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004 Jan 1;11(Pt 1):49-52. doi: 10.1107/s0909049503023938. Epub 2003 Nov 28. J Synchrotron Radiat. 2004. PMID: 14646132
-
Experimental Phasing: Substructure Solution and Density Modification as Implemented in SHELX.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:357-376. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7000-1_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28573581 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for replication origin unwinding by an initiator primase of plasmid ColE2-P9: duplex DNA unwinding by a single protein.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3601-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595645. Epub 2014 Dec 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25538245 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for lack of ADP-ribosyltransferase activity in poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-13/zinc finger antiviral protein.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 20;290(12):7336-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.630160. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25635049 Free PMC article.
-
Cas5d protein processes pre-crRNA and assembles into a cascade-like interference complex in subtype I-C/Dvulg CRISPR-Cas system.Structure. 2012 Sep 5;20(9):1574-84. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.06.016. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Structure. 2012. PMID: 22841292 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of the tetratricopeptide repeat domains of kinesin light chains: insight into cargo recognition mechanisms.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33943. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033943. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470497 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular architecture of the bacteriophage T4 neck.J Mol Biol. 2013 May 27;425(10):1731-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.02.012. Epub 2013 Feb 19. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23434847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams, J. P., Leslie, A. G. W., Lutter, R. & Walker, J. E. (1994). Nature (London), 370, 621–628. - PubMed
-
- American Type Culture Collection (1992). Catalogue of Bacteria and Bacteriophages, 18th ed., pp. 271–272.
-
- Bernstein, F. C., Koetzle, T. F., Williams, G. J. B., Meyer, E. F., Brice, M. D., Rodgers, J. R., Kennard, O., Shimanouchi, T. & Tasumi, M. (1977). J. Mol. Biol.112, 535–542. - PubMed
-
- Blundell, T. L. & Johnson, L. N. (1976). Protein Crystallography, p. 368. New York: Academic Press.
-
- Buerger, M. J. (1970). Contemporary Crystallography. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

