A cloning method to identify caspases and their regulators in yeast: identification of Drosophila IAP1 as an inhibitor of the Drosophila caspase DCP-1
- PMID: 10077606
- PMCID: PMC15864
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.2885
A cloning method to identify caspases and their regulators in yeast: identification of Drosophila IAP1 as an inhibitor of the Drosophila caspase DCP-1
Abstract
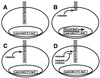
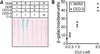
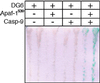
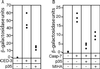
Site-specific proteases play critical roles in regulating many cellular processes. To identify novel site-specific proteases, their regulators, and substrates, we have designed a general reporter system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which a transcription factor is linked to the intracellular domain of a transmembrane protein by protease cleavage sites. Here, we explore the efficacy of this approach by using caspases, a family of aspartate-specific cysteine proteases, as a model. Introduction of an active caspase into cells that express a caspase-cleavable reporter results in the release of the transcription factor from the membrane and subsequent activation of a nuclear reporter. We show that known caspases activate the reporter, that an activator of caspase activity stimulates reporter activation in the presence of an otherwise inactive caspase, and that caspase inhibitors suppress caspase-dependent reporter activity. We also find that, although low or moderate levels of active caspase expression do not compromise yeast cell growth, higher level expression leads to lethality. We have exploited this observation to isolate clones from a Drosophila embryo cDNA library that block DCP-1 caspase-dependent yeast cell death. Among these clones, we identified the known cell death inhibitor DIAP1. We showed, by using bacterially synthesized proteins, that glutathione S-transferase-DIAP1 directly inhibits DCP-1 caspase activity but that it had minimal effect on the activity of a predomainless version of a second Drosophila caspase, drICE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1.EMBO J. 2000 Feb 15;19(4):598-611. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.598. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10675329 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila inhibitor of apoptosis D-IAP1 suppresses cell death induced by the caspase drICE.FEBS Lett. 1998 Nov 27;440(1-2):243-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)01465-3. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9862464
-
Stage-specific regulation of caspase activity in drosophila oogenesis.Dev Biol. 2003 Aug 1;260(1):113-23. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00240-9. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 12885559
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in Drosophila: gatekeepers of death.Apoptosis. 2009 Aug;14(8):950-60. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0358-2. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Apoptosis. 2009. PMID: 19495985 Review.
-
Autophagic programmed cell death in Drosophila.Cell Death Differ. 2003 Sep;10(9):940-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401280. Cell Death Differ. 2003. PMID: 12934068 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional and biochemical characterization of the baculovirus caspase inhibitor MaviP35.Cell Death Dis. 2011 Dec 15;2(12):e242. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.127. Cell Death Dis. 2011. PMID: 22170098 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1.EMBO J. 2000 Feb 15;19(4):598-611. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.598. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10675329 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CED-3 substrates by a yeast-based screening method.Mol Biotechnol. 2004 May;27(1):1-6. doi: 10.1385/MB:27:1:01. Mol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15122042
-
Vaccinia Virus Encodes a Novel Inhibitor of Apoptosis That Associates with the Apoptosome.J Virol. 2017 Nov 14;91(23):e01385-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01385-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28904196 Free PMC article.
-
IAP-antagonists exhibit non-redundant modes of action through differential DIAP1 binding.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 15;22(24):6642-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg617. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14657035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alnemri E S, Livingston D J, Nicholson D W, Salvesen G, Thornberry N A, Wong W W, Yuan J. Cell. 1996;87:171. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson D W, Thornberry N. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Salvesen G S, Dixit V M. Cell. 1997;91:443–446. - PubMed
-
- Thornberry N A, Lazebnik Y. Science. 1998;281:1312–1316. - PubMed
-
- Cryns V, Yuan J. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1551–1570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

