RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 10066249
- PMCID: PMC6782583
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-06-01959.1999
RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
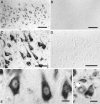
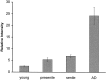
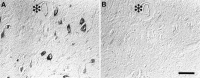
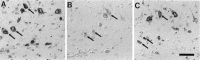
In this study we used an in situ approach to identify the oxidized nucleosides 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8OHdG) and 8-hydroxyguanosine (8OHG), markers of oxidative damage to DNA and RNA, respectively, in cases of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The goal was to determine whether nuclear and mitochondrial DNA as well as RNA is damaged in AD. Immunoreactivity with monoclonal antibodies 1F7 or 15A3 recognizing both 8OHdG and 8OHG was prominent in the cytoplasm and to a lesser extent in the nucleolus and nuclear envelope in neurons within the hippocampus, subiculum, and entorhinal cortex as well as frontal, temporal, and occipital neocortex in cases of AD, whereas similar structures were immunolabeled only faintly in controls. Relative density measurement showed that there was a significant increase (p < 0.0001) in 8OHdG and 8OHG immunoreactivity with 1F7 in cases of AD (n = 22) as compared with senile (n = 13), presenile (n = 10), or young controls (n = 4). Surprisingly, the oxidized nucleoside was associated predominantly with RNA because immunoreaction was diminished greatly by preincubation in RNase but only slightly by DNase. This is the first evidence of increased RNA oxidation restricted to vulnerable neurons in AD. The subcellular localization of damaged RNA showing cytoplasmic predominance is consistent with the hypothesis that mitochondria may be a major source of reactive oxygen species that cause oxidative damage in AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuronal RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of familial Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2004 Oct;17(1):108-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.06.003. Neurobiol Dis. 2004. PMID: 15350971
-
Parkinson's disease is associated with oxidative damage to cytoplasmic DNA and RNA in substantia nigra neurons.Am J Pathol. 1999 May;154(5):1423-9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65396-5. Am J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10329595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The earliest stage of cognitive impairment in transition from normal aging to Alzheimer disease is marked by prominent RNA oxidation in vulnerable neurons.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2012 Mar;71(3):233-41. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e318248e614. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22318126 Free PMC article.
-
RNA oxidation in Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative disorders.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Jul;118(1):151-66. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0508-1. Epub 2009 Mar 7. Acta Neuropathol. 2009. PMID: 19271225 Review.
-
Metabolic, metallic, and mitotic sources of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2000 Fall;2(3):413-20. doi: 10.1089/15230860050192198. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2000. PMID: 11229355 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of RNA damage under oxidative stress in Escherichia coli.Biol Chem. 2012 Mar;393(3):123-32. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2011-0247. Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22718628 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium Benzoate Exerts Neuroprotective Effect by Improving Mitochondrial Function, Attenuating Reactive Oxygen Species, and Protecting Cognition and Memory in an Animal Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2022 Sep 20;6(1):557-575. doi: 10.3233/ADR-220025. eCollection 2022. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2022. PMID: 36275418 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal mRNA translation in neurological disorders.RNA Biol. 2021 Jul;18(7):936-961. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1822638. Epub 2020 Sep 29. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32988274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Feb 15;7(5):376-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.05.009. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25774178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative imbalance in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2005;31(1-3):205-17. doi: 10.1385/MN:31:1-3:205. Mol Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 15953822 Review.
References
-
- Bancroft JD, Stevens A. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 1996. Fourth edition, New York: Churchill-Livingstone.
-
- Beal MF. Aging, energy, and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Claycamp HG. Phenol sensitization of DNA to subsequent oxidative damage in 8-hydroxyguanine assays. Carcinogenesis. 1992;13:1289–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
