Nuclear foci of mammalian recombination proteins are located at single-stranded DNA regions formed after DNA damage
- PMID: 10051570
- PMCID: PMC26712
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.1921
Nuclear foci of mammalian recombination proteins are located at single-stranded DNA regions formed after DNA damage
Abstract
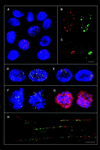
A sensitive and rapid in situ method was developed to visualize sites of single-stranded (ss) DNA in cultured cells and in experimental test animals. Anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibody recognizes the halogenated base analog incorporated into chromosomal DNA only when substituted DNA is in the single strand form. After treatment of cells with DNA-damaging agents or gamma irradiation, ssDNA molecules form nuclear foci in a dose-dependent manner within 60 min. The mammalian recombination protein Rad51 and the replication protein A then accumulate at sites of ssDNA and form foci, suggesting that these are sites of recombinational DNA repair.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear foci of mammalian Rad51 recombination protein in somatic cells after DNA damage and its localization in synaptonemal complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2298-302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2298. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7892263 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin-bound PCNA complex formation triggered by DNA damage occurs independent of the ATM gene product in human cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Mar 15;29(6):1341-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.6.1341. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11239001 Free PMC article.
-
Sequestration of mammalian Rad51-recombination protein into micronuclei.J Cell Biol. 1999 Jan 11;144(1):11-20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.1.11. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9885240 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CDKN1A (p21) binding to sites of heavy-ion-induced damage: colocalization with proteins involved in DNA repair.Int J Radiat Biol. 2002 Feb;78(2):75-88. doi: 10.1080/09553000110090007. Int J Radiat Biol. 2002. PMID: 11779358
-
Formation of strand breaks in the DNA of gamma-irradiated chromatin.Radiat Environ Biophys. 1987;26(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/BF01211361. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1987. PMID: 3588834
Cited by
-
Tracking chromatid segregation to identify human cardiac stem cells that regenerate extensively the infarcted myocardium.Circ Res. 2012 Sep 14;111(7):894-906. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.273649. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Circ Res. 2012. Retraction in: Circ Res. 2019 Feb 15;124(4):e29. doi: 10.1161/RES.0000000000000253 PMID: 22851539 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Radiation-induced double-strand breaks require ATM but not Artemis for homologous recombination during S-phase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8336-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks604. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22730303 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of human replication protein A (RPA): from DNA replication to DNA damage and stress responses.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Aug;208(2):267-73. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20622. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16523492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cellular phenotype of Roberts syndrome fibroblasts as revealed by ectopic expression of ESCO2.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 7;4(9):e6936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006936. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19738907 Free PMC article.
-
ADAD2 regulates heterochromatin in meiotic and post-meiotic male germ cells via translation of MDC1.J Cell Sci. 2022 Feb 15;135(4):jcs259196. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259196. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 35191498 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

