Cyclin D-CDK subunit arrangement is dependent on the availability of competing INK4 and p21 class inhibitors
- PMID: 10022865
- PMCID: PMC83971
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1775
Cyclin D-CDK subunit arrangement is dependent on the availability of competing INK4 and p21 class inhibitors
Abstract
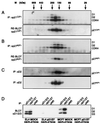
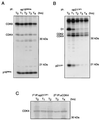
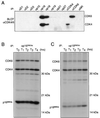
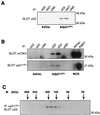
The D-type cyclins and their major kinase partners CDK4 and CDK6 regulate G0-G1-S progression by contributing to the phosphorylation and inactivation of the retinoblastoma gene product, pRB. Assembly of active cyclin D-CDK complexes in response to mitogenic signals is negatively regulated by INK4 family members. Here we show that although all four INK4 proteins associate with CDK4 and CDK6 in vitro, only p16(INK4a) can form stable, binary complexes with both CDK4 and CDK6 in proliferating cells. The other INK4 family members form stable complexes with CDK6 but associate only transiently with CDK4. Conversely, CDK4 stably associates with both p21(CIP1) and p27(KIP1) in cyclin-containing complexes, suggesting that CDK4 is in equilibrium between INK4 and p21(CIP1)- or p27(KIP1)-bound states. In agreement with this hypothesis, overexpression of p21(CIP1) in 293 cells, where CDK4 is bound to p16(INK4a), stimulates the formation of ternary cyclin D-CDK4-p21(CIP1) complexes. These data suggest that members of the p21 family of proteins promote the association of D-type cyclins with CDKs by counteracting the effects of INK4 molecules.
Figures
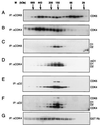
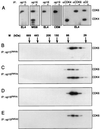
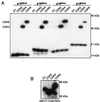
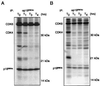
Similar articles
-
Induced expression of p16(INK4a) inhibits both CDK4- and CDK2-associated kinase activity by reassortment of cyclin-CDK-inhibitor complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):1981-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.1981. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10022885 Free PMC article.
-
Kip/Cip and Ink4 Cdk inhibitors cooperate to induce cell cycle arrest in response to TGF-beta.Genes Dev. 1995 Aug 1;9(15):1831-45. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.15.1831. Genes Dev. 1995. PMID: 7649471
-
Differential effects of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p27(Kip1), p21(Cip1), and p16(Ink4) on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation.Circulation. 2000 May 2;101(17):2022-5. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.17.2022. Circulation. 2000. PMID: 10790340
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
-
Role of cyclin-dependent kinases and their inhibitors in cellular differentiation and development.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;227:57-103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71941-7_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9479826 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Ras promotes p21(Waf1/Cip1) protein stability via a cyclin D1-imposed block in proteasome-mediated degradation.EMBO J. 2003 May 1;22(9):2036-46. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg189. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12727871 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle checkpoints and their inactivation in human cancer.Cell Prolif. 2000 Oct;33(5):261-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2000.00191.x. Cell Prolif. 2000. PMID: 11063129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK6-a review of the past and a glimpse into the future: from cell-cycle control to transcriptional regulation.Oncogene. 2016 Jun 16;35(24):3083-91. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.407. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26500059 Review.
-
Regulation of CDK4.Cell Div. 2006 Nov 8;1:25. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-1-25. Cell Div. 2006. PMID: 17092340 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CDK4 activity by a novel CDK4-binding protein, p34(SEI-1).Genes Dev. 1999 Nov 15;13(22):3027-33. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.22.3027. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10580009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aagaard L, Lukas J, Bartkova J, Kjerulff A-A, Strauss M, Bartek J. Aberrations of p16Ink4 and retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor genes occur in distinct sub-sets of human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1995;61:115–120. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D, Holder A, Dickson C, Peters G. CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct set of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1994;9:71–79. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Parry D, Bonetta L, Vousden K, Dickson C, Peters G. Absence of cyclin D/cdk complexes in cells lacking functional retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1994;9:1633–1640. - PubMed
-
- Brookes S, Lammie G, Schuuring E, de Boer C, Michalides R, Dickson C, Peters G. Amplified region of chromosome band 11q13 in breast and squamous cell carcinomas encompasses three CpG islands telomeric of FGF3, including the expressed gene EMS1. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993;6:222–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
