Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain
- PMID: 9887101
- PMCID: PMC316370
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.1.76
Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain
Abstract
Transcription factor Nrf2 is essential for the antioxidant responsive element (ARE)-mediated induction of phase II detoxifying and oxidative stress enzyme genes. Detailed analysis of differential Nrf2 activity displayed in transfected cell lines ultimately led to the identification of a new protein, which we named Keap1, that suppresses Nrf2 transcriptional activity by specific binding to its evolutionarily conserved amino-terminal regulatory domain. The closest homolog of Keap1 is a Drosophila actin-binding protein called Kelch, implying that Keap1 might be a Nrf2 cytoplasmic effector. We then showed that electrophilic agents antagonize Keap1 inhibition of Nrf2 activity in vivo, allowing Nrf2 to traverse from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and potentiate the ARE response. We postulate that Keap1 and Nrf2 constitute a crucial cellular sensor for oxidative stress, and together mediate a key step in the signaling pathway that leads to transcriptional activation by this novel Nrf2 nuclear shuttling mechanism. The activation of Nrf2 leads in turn to the induction of phase II enzyme and antioxidative stress genes in response to electrophiles and reactive oxygen species.
Figures

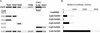
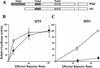
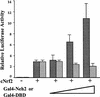


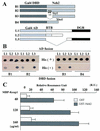
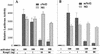
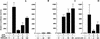
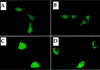
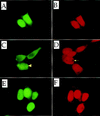
Similar articles
-
Evolutionary conserved N-terminal domain of Nrf2 is essential for the Keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 15;433(2):342-50. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.10.012. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581590 Review.
-
Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles.Free Radic Biol Med. 2004 May 15;36(10):1208-13. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.075. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004. PMID: 15110385 Review.
-
Protection against electrophile and oxidant stress by induction of the phase 2 response: fate of cysteines of the Keap1 sensor modified by inducers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 17;101(7):2040-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307301101. Epub 2004 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14764894 Free PMC article.
-
The Keap1 BTB/POZ dimerization function is required to sequester Nrf2 in cytoplasm.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 27;277(39):36544-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206530200. Epub 2002 Jul 26. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12145307
-
Discovery of the negative regulator of Nrf2, Keap1: a historical overview.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010 Dec 1;13(11):1665-78. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3222. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010. PMID: 20446768 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimizing Oxidative Stress in the Lens: Alternative Measures for Elevating Glutathione in the Lens to Protect against Cataract.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 1;13(10):1193. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101193. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of exogenous taurine supplementation on the growth, antioxidant capacity, intestine immunity, and resistance against Streptococcus agalactiae in juvenile golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) fed with a low-fishmeal diet.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 14;13:1036821. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1036821. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311806 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK Enhances Transcription of Selected Nrf2 Target Genes via Negative Regulation of Bach1.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 14;8:628. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00628. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32760724 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific Role of Macrophages in Noninfectious Inflammatory Disorders.Biomedicines. 2020 Oct 9;8(10):400. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100400. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33050138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress and immunity in poultry: light management and nanotechnology as effective immune enhancers to fight stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021 May;26(3):457-472. doi: 10.1007/s12192-021-01204-6. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021. PMID: 33847921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alam J, Camhi S, Choi AMK. Identification of a second region upstream of the mouse heme oxygenase-1 gene that functions as a basal level and inducer-dependent transcriptional enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:11977–11984. - PubMed
-
- Albagli O, Dhordain P, Deweindt C, Lecocq G, Leprince D. The BTB/POZ domain: A new protein-protein interaction motif common to DNA- and actin-binding proteins. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:1193–1198. - PubMed
-
- Ames BN. Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative disease. Science. 1983;221:1256–1264. - PubMed
-
- Bannai S. Induction of cystine and glutamate transport activity in human fibroblasts by diethylmaleate and other electrophilic agents. J Biol Chem. 1984;264:2435–2440. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell VJ, Treisman R. The POZ domain: A conserved protein–protein interaction motif. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:1664–1677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
