Sequestration of mammalian Rad51-recombination protein into micronuclei
- PMID: 9885240
- PMCID: PMC2148121
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.144.1.11
Sequestration of mammalian Rad51-recombination protein into micronuclei
Abstract
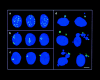
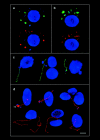
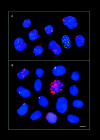
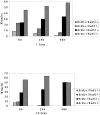
The mammalian Rad51 protein is involved in homologous recombination and in DNA damage repair. Its nuclear distribution after DNA damage is highly dynamic, and distinct foci of Rad51 protein, distributed throughout the nuclear volume, are induced within a few hours after gamma irradiation; these foci then coalesce into larger clusters. Rad51-positive cells do not undergo DNA replication. Rad51 foci colocalize with both replication protein A and sites of unscheduled DNA repair synthesis and may represent a nuclear domain for recombinational DNA repair. By 24 h postirradiation, most foci are sequestered into micronuclei or assembled into Rad51-coated DNA fibers. These micronuclei and DNA fibers display genome fragmentation typical of apoptotic cell death. Other repair proteins, such as Rad52 and Gadd45, are not eliminated from the nucleus. DNA double strand breaks in repair-deficient cells or induced by the clastogen etoposide are also accompanied by the sequestering of Rad51 protein before cell death. The spindle poison colcemid causes cell cycle arrest and Rad51-foci formation without directly damaging DNA. Collectively, these observations suggest that mammalian Rad51 protein associates with damaged DNA and/or with DNA that is temporarily or irreversibly unable to replicate and these foci may subsequently be eliminated from the nucleus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ionizing radiation-induced foci formation of mammalian Rad51 and Rad54 depends on the Rad51 paralogs, but not on Rad52.Mutat Res. 2005 Jul 1;574(1-2):34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.01.020. Epub 2005 Apr 9. Mutat Res. 2005. PMID: 15914205
-
Nuclear foci of mammalian Rad51 recombination protein in somatic cells after DNA damage and its localization in synaptonemal complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2298-302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2298. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7892263 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear dynamics of RAD52 group homologous recombination proteins in response to DNA damage.EMBO J. 2002 Apr 15;21(8):2030-7. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.8.2030. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11953322 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of higher-order nuclear Rad51 structures is functionally linked to p21 expression and protection from DNA damage-induced apoptosis.J Cell Sci. 2002 Jan 1;115(Pt 1):153-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.1.153. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11801733
-
Assembly of RecA-like recombinases: distinct roles for mediator proteins in mitosis and meiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 17;98(15):8411-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.121046198. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11459983 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term fate of etoposide-induced micronuclei and micronucleated cells in Hela-H2B-GFP cells.Arch Toxicol. 2020 Oct;94(10):3553-3561. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02840-0. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32681187 Free PMC article.
-
RAD51 supports spontaneous non-homologous recombination in mammalian cells, but not the corresponding process induced by topoisomerase inhibitors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Feb 1;29(3):662-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.3.662. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11160887 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and localization of the Bloom syndrome protein in response to DNA damage.J Cell Biol. 2001 Apr 16;153(2):367-80. doi: 10.1083/jcb.153.2.367. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11309417 Free PMC article.
-
RAP80-directed tuning of BRCA1 homologous recombination function at ionizing radiation-induced nuclear foci.Genes Dev. 2011 Apr 1;25(7):685-700. doi: 10.1101/gad.2011011. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21406551 Free PMC article.
-
The essential functions of human Rad51 are independent of ATP hydrolysis.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6891-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6891. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albala JS, Thelen MP, Prange C, Fan W, Christensen M, Thompson LH, Lennon GG. Identification of a novel human RAD51 homolog, RAD51B. . Genomics. 1997;46:476–479. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, Benson FE, West SC. Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro. Cell. 1996;87:757–766. - PubMed
-
- Benson FE, Baumann P, West SC. Synergistic actions of Rad51 and Rad52 in recombination and DNA repair. Nature. 1998;391:401–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

