Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [correction of tris-phosphate] activation of inositol trisphosphate [correction of tris-phosphate] receptor Ca2+ channel by ligand tuning of Ca2+ inhibition
- PMID: 9861054
- PMCID: PMC28128
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15821
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate [correction of tris-phosphate] activation of inositol trisphosphate [correction of tris-phosphate] receptor Ca2+ channel by ligand tuning of Ca2+ inhibition
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999 Mar 16;96(6):3330
Abstract
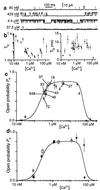
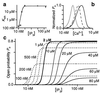
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) [corrected] binding to its receptors (IP3R) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) activates Ca2+ release from the ER lumen to the cytoplasm, generating complex cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration signals including temporal oscillations and propagating waves. IP3-mediated Ca2+ release is also controlled by cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration with both positive and negative feedback. Single-channel properties of the IP3R in its native ER membrane were investigated by patch clamp electrophysiology of isolated Xenopus oocyte nuclei to determine the dependencies of IP3R on cytoplasmic Ca2+ and IP3 concentrations under rigorously defined conditions. Instead of the expected narrow bell-shaped cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) response centered at approximately 300 nM-1 microM, the open probability remained elevated (approximately 0.8) in the presence of saturating levels (10 microM) of IP3, even as [Ca2+]i was raised to high concentrations, displaying two distinct types of functional Ca2+ binding sites: activating sites with half-maximal activating [Ca2+]i (Kact) of 210 nM and Hill coefficient (Hact) approximately 2; and inhibitory sites with half-maximal inhibitory [Ca2+]i (Kinh) of 54 microM and Hill coefficient (Hinh) approximately 4. Lowering IP3 concentration was without effect on Ca2+ activation parameters or Hinh, but decreased Kinh with a functional half-maximal activating IP3 concentration (KIP3) of 50 nM and Hill coefficient (HIP3) of 4 for IP3. These results demonstrate that Ca2+ is a true receptor agonist, whereas the sole function of IP3 is to relieve Ca2+ inhibition of IP3R. Allosteric tuning of Ca2+ inhibition by IP3 enables the individual IP3R Ca2+ channel to respond in a graded fashion, which has implications for localized and global cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration signaling and quantal Ca2+ release.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation by Ca2+ and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) of single recombinant type 3 InsP3 receptor channels. Ca2+ activation uniquely distinguishes types 1 and 3 insp3 receptors.J Gen Physiol. 2001 May;117(5):435-46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.117.5.435. J Gen Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11331354 Free PMC article.
-
Single-channel kinetics, inactivation, and spatial distribution of inositol trisphosphate (IP3) receptors in Xenopus oocyte nucleus.J Gen Physiol. 1997 May;109(5):571-87. doi: 10.1085/jgp.109.5.571. J Gen Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9154905 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of calcium release by immunoaffinity-purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in reconstituted lipid vesicles.J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):19046-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.19046. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7642567
-
Inositol trisphosphate receptor mediated spatiotemporal calcium signalling.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):190-6. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80027-1. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7612270 Review.
-
Structure and function of IP3 receptors.Semin Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;5(4):273-81. doi: 10.1006/scel.1994.1033. Semin Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7994011 Review.
Cited by
-
Direct association of ligand-binding and pore domains in homo- and heterotetrameric inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors.EMBO J. 2000 Oct 16;19(20):5450-9. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5450. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11032812 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand sensitivity of type-1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is enhanced by the D2594K mutation.Pflugers Arch. 2023 May;475(5):569-581. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02796-x. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 36881190 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and function of a calmodulin-apocalmodulin-binding domain in the N-terminal part of the type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor.Biochem J. 2002 Jul 1;365(Pt 1):269-77. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020144. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 11955285 Free PMC article.
-
Redox-regulated heterogeneous thresholds for ligand recruitment among InsP3R Ca2+-release channels.Biophys J. 2010 Jul 21;99(2):407-16. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.034. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20643058 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of smooth muscle excitation and contraction.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008 May;20 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):39-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01108.x. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2008. PMID: 18402641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berridge M J. Nature (London) 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Meyer T, Stryer L. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:153–174. - PubMed
-
- Toescu E C. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G173–G185. - PubMed
-
- Bootman M D. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1994;98:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Parys J B, Missiaen L, De Smedt H, Sienaert I, Casteels R. Pflügers Arch. 1996;432:359–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

