Cloning of the cDNA encoding the urotensin II precursor in frog and human reveals intense expression of the urotensin II gene in motoneurons of the spinal cord
- PMID: 9861051
- PMCID: PMC28125
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15803
Cloning of the cDNA encoding the urotensin II precursor in frog and human reveals intense expression of the urotensin II gene in motoneurons of the spinal cord
Abstract
Urotensin II (UII) is a cyclic peptide initially isolated from the caudal neurosecretory system of teleost fish. Subsequently, UII has been characterized from a frog brain extract, indicating that a gene encoding a UII precursor is also present in the genome of a tetrapod. Here, we report the characterization of the cDNAs encoding frog and human UII precursors and the localization of the corresponding mRNAs. In both frog and human, the UII sequence is located at the C-terminal position of the precursor. Human UII is composed of only 11 amino acid residues, while fish and frog UII possess 12 and 13 amino acid residues, respectively. The cyclic region of UII, which is responsible for the biological activity of the peptide, has been fully conserved from fish to human. Northern blot and dot blot analysis revealed that UII precursor mRNAs are found predominantly in the frog and human spinal cord. In situ hybridization studies showed that the UII precursor gene is actively expressed in motoneurons. The present study demonstrates that UII, which has long been regarded as a peptide exclusively produced by the urophysis of teleost fish, is actually present in the brain of amphibians and mammals. The fact that evolutionary pressure has acted to conserve fully the biologically active sequence of UII suggests that the peptide may exert important physiological functions in humans.
Figures
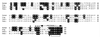


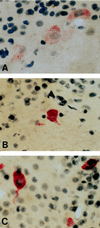
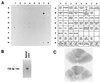

Similar articles
-
Cloning, sequence analysis and tissue distribution of the mouse and rat urotensin II precursors.FEBS Lett. 1999 Aug 20;457(1):28-32. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01003-0. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10486557
-
Urotensin II in the central nervous system of the frog Rana ridibunda: immunohistochemical localization and biochemical characterization.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Jan 8;364(2):324-39. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960108)364:2<324::AID-CNE10>3.0.CO;2-P. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8788253
-
Androgenic down-regulation of urotensin II precursor, urotensin II-related peptide precursor and androgen receptor mRNA in the mouse spinal cord.Neuroscience. 2005;132(3):689-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.045. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15837130
-
Urotensin II, from fish to human.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010 Jul;1200:53-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05514.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010. PMID: 20633133 Review.
-
Liberation of urotensin II from the teleost urophysis: an historical overview.Peptides. 2008 May;29(5):651-7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.04.021. Epub 2007 May 6. Peptides. 2008. PMID: 17544546 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of UII/UTR system relieves acute inflammation of liver through preventing activation of NF-κB pathway in ALF mice.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 3;8(6):e64895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064895. Print 2014. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23755157 Free PMC article.
-
Vasoconstrictive effects of endothelin-1, endothelin-3, and urotensin II in isolated perfused human lungs and isolated human pulmonary arteries.Thorax. 2004 May;59(5):401-7. doi: 10.1136/thx.2003.011197. Thorax. 2004. PMID: 15115867 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of nuclear urotensin-II binding sites in rat heart.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 May;166(1):243-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01710.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22044114 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Classic Adrenal Secretagogues on mRNA Levels of Urotensin II and Its Receptor in Adrenal Gland of Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13412. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713412. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686217 Free PMC article.
-
Urotensin-II: More Than a Mediator for Kidney.Int J Nephrol. 2012;2012:249790. doi: 10.1155/2012/249790. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Int J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 23094156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bern H A, Pearson D, Larson B A, Nishioka R S. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:533–552. - PubMed
-
- Lederis K, Letter A, McMaster D, Moore G, Schlesinger D. Science. 1982;218:162–164. - PubMed
-
- Conlon J M, Tostivint H, Vaudry H. Regul Pept. 1997;69:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Waugh D, Conlon J M. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1993;92:419–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

