hnRNP A1 recruited to an exon in vivo can function as an exon splicing silencer
- PMID: 9858549
- PMCID: PMC83883
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.1.251
hnRNP A1 recruited to an exon in vivo can function as an exon splicing silencer
Abstract
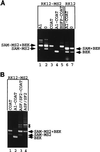
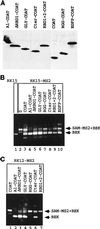
Some exons contain exon splicing silencers. Their activity is frequently balanced by that of splicing enhancers, and this is important to ensure correct relative levels of alternatively spliced mRNAs. Using an immunoprecipitation and UV-cross-linking assay, we show that RNA molecules containing splicing silencers from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat exon 2 or the human fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 K-SAM exon bind to hnRNP A1 in HeLa cell nuclear extracts better than the corresponding RNA molecule without a silencer. Two different point mutations which abolish the K-SAM exon splicing silencer's activity reduce hnRNP A1 binding twofold. Recruitment of hnRNP A1 in the form of a fusion with bacteriophage MS2 coat protein to a K-SAM exon whose exon splicing silencer has been replaced by a coat binding site efficiently represses splicing of the exon in vivo. Recruitment of only the glycine-rich C-terminal domain of hnRNP A1, which is capable of interactions with other proteins, is sufficient to repress exon splicing. Our results show that hnRNP A1 can function to repress splicing, and they suggest that at least some exon splicing silencers could work by recruiting hnRNP A1.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A second exon splicing silencer within human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat exon 2 represses splicing of Tat mRNA and binds protein hnRNP H.J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 2;276(44):40464-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104070200. Epub 2001 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11526107
-
Exon identity established through differential antagonism between exonic splicing silencer-bound hnRNP A1 and enhancer-bound SR proteins.Mol Cell. 2001 Dec;8(6):1351-61. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00409-9. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11779509
-
hnRNP A1 and the SR proteins ASF/SF2 and SC35 have antagonistic functions in splicing of beta-tropomyosin exon 6B.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 10;279(37):38249-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405377200. Epub 2004 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15208309
-
A comprehensive understanding of hnRNP A1 role in cancer: new perspectives on binding with noncoding RNA.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Mar;30(3):394-403. doi: 10.1038/s41417-022-00571-1. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 36460805 Review.
-
Idiosyncrasies of hnRNP A1-RNA recognition: Can binding mode influence function.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Feb;86:150-161. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 29625167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of alternative RNA splicing by exon definition and exon sequences in viral and mammalian gene expression.J Biomed Sci. 2004 May-Jun;11(3):278-94. doi: 10.1007/BF02254432. J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 15067211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of exon skipping by high-affinity hnRNP A1-binding sites and by intron elements that repress splice site utilization.EMBO J. 1999 Apr 1;18(7):1939-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.7.1939. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10202157 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the two-RRM domain of hnRNP A1 (UP1) complexed with single-stranded telomeric DNA.Genes Dev. 1999 May 1;13(9):1102-15. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.9.1102. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10323862 Free PMC article.
-
Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 3 and Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1 Regulate Alternative RNA Splicing and Gene Expression of Human Papillomavirus 18 through Two Functionally Distinguishable cis Elements.J Virol. 2016 Sep 29;90(20):9138-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00965-16. Print 2016 Oct 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27489271 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging the alternative silencing of FGFR2 exon IIIb in vivo.RNA. 2006 Dec;12(12):2073-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.248506. Epub 2006 Oct 26. RNA. 2006. PMID: 17068207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams M D, Tarng R S, Rio D C. The alternative splicing factor PSI regulates P-element third intron splicing in vivo. Genes Dev. 1997;11:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Baba-Aissa F, Van Den Bosch L, Wuytack F, Raeymaekers L, Casteels R. Regulation of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) 2 gene transcript in neuronal cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;55:92–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
