Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type
- PMID: 9852584
- PMCID: PMC6793365
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-24-10464.1998
Synaptic modifications in cultured hippocampal neurons: dependence on spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type
Abstract
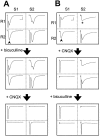
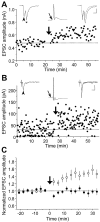
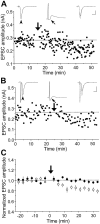
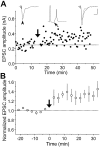
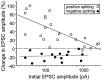
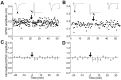
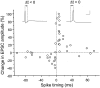
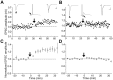
In cultures of dissociated rat hippocampal neurons, persistent potentiation and depression of glutamatergic synapses were induced by correlated spiking of presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. The relative timing between the presynaptic and postsynaptic spiking determined the direction and the extent of synaptic changes. Repetitive postsynaptic spiking within a time window of 20 msec after presynaptic activation resulted in long-term potentiation (LTP), whereas postsynaptic spiking within a window of 20 msec before the repetitive presynaptic activation led to long-term depression (LTD). Significant LTP occurred only at synapses with relatively low initial strength, whereas the extent of LTD did not show obvious dependence on the initial synaptic strength. Both LTP and LTD depended on the activation of NMDA receptors and were absent in cases in which the postsynaptic neurons were GABAergic in nature. Blockade of L-type calcium channels with nimodipine abolished the induction of LTD and reduced the extent of LTP. These results underscore the importance of precise spike timing, synaptic strength, and postsynaptic cell type in the activity-induced modification of central synapses and suggest that Hebb's rule may need to incorporate a quantitative consideration of spike timing that reflects the narrow and asymmetric window for the induction of synaptic modification.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of induction and expression of long-term depression at GABAergic synapses in the neonatal rat hippocampus.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):7568-77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07568.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460263 Free PMC article.
-
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity of neocortical excitatory synapses on inhibitory interneurons depends on target cell type.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 5;27(36):9711-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2513-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17804631 Free PMC article.
-
Coincident pre- and postsynaptic activity modifies GABAergic synapses by postsynaptic changes in Cl- transporter activity.Neuron. 2003 Aug 28;39(5):807-20. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00507-5. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 12948447
-
Natural patterns of activity and long-term synaptic plasticity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000 Apr;10(2):172-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00076-3. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10753798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associative synaptic plasticity in hippocampus and visual cortex: cellular mechanisms and functional implications.Rev Neurosci. 1996 Jan-Mar;7(1):29-46. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.1996.7.1.29. Rev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8736677 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term depression and long-term plasticity together tune sensitive range of synaptic plasticity.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Sep 25;16(9):e1008265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008265. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32976516 Free PMC article.
-
Memory consolidation and improvement by synaptic tagging and capture in recurrent neural networks.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 3;4(1):275. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01778-y. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33658641 Free PMC article.
-
Place cells, grid cells, and memory.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Feb 2;7(2):a021808. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021808. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25646382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory-enhancing amygdala stimulation elicits gamma synchrony in the hippocampus.Behav Neurosci. 2015 Jun;129(3):244-56. doi: 10.1037/bne0000052. Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26030426 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of different synchronization modes and synaptic plasticity in a system of class I neurons.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 16;12(1):19631. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24001-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36385488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arancio O, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Activity-dependent long-term enhancement of transmitter release by presynaptic 3′,5′-cyclic GMP in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1995;376:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. Presynaptic mechanism for long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1990;346:724–729. - PubMed
-
- Bell CC, Han VZ, Sugawara Y, Grant K. Synaptic plasticity in a cerebellum-like structure depends on temporal order. Nature. 1997;387:278–281. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TV, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
