Expression of myogenin during embryogenesis is controlled by Six/sine oculis homeoproteins through a conserved MEF3 binding site
- PMID: 9826681
- PMCID: PMC24354
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.24.14220
Expression of myogenin during embryogenesis is controlled by Six/sine oculis homeoproteins through a conserved MEF3 binding site
Abstract
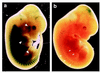
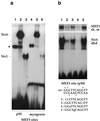
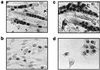
Myogenin, one of the MyoD family of proteins, is expressed early during somitogenesis and is required for myoblast fusion in vivo. Previous studies in transgenic mice have shown that a 184-bp myogenin promoter fragment is sufficient to correctly drive expression of a beta-galactosidase transgene during embryogenesis. We show here that mutation of one of the DNA motifs present in this region, the MEF3 motif, abolished correct expression of this beta-galactosidase transgene. We have found that the proteins that bind to the MEF3 site are homeoproteins of the Six/sine oculis family. Antibodies directed specifically against Six1 or Six4 proteins reveal that each of these proteins is present in the embryo when myogenin is activated and constitutes a muscle-specific MEF3-binding activity in adult muscle nuclear extracts. Both of these proteins accumulate in the nucleus of C2C12 myogenic cells, and transient transfection experiments confirm that Six1 and Six4 are able to transactivate a reporter gene containing MEF3 sites. Altogether these results establish Six homeoproteins as a family of transcription factors controlling muscle formation through activation of one of its key regulators, myogenin.
Figures
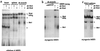

Similar articles
-
Six and Eya expression during human somitogenesis and MyoD gene family activation.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(3):255-64. doi: 10.1023/a:1020990825644. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12500905
-
Overexpression of Six1 leads to retardation of myogenic differentiation in C2C12 myoblasts.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jan;40(1):217-23. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2052-7. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23079703
-
Muscle-specific expression of myogenin in zebrafish embryos is controlled by multiple regulatory elements in the promoter.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jan;134(1):123-34. doi: 10.1016/s1096-4959(02)00194-x. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12524040
-
Activation of muscle-specific transcription by myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins.Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1992;46:331-41. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1992. PMID: 1341046 Review.
-
Myogenesis control by SIX transcriptional complexes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug;104:51-64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32247726 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of male sex determination: genital ridge formation and Sry activation in mice.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Dec;71(24):4781-802. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1703-3. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25139092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Six1 gene suppresses proliferation and enhances expression of fast-type muscle genes in C2C12 myoblasts.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;380(1-2):23-32. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1653-3. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23613228
-
Discovery, optimization and validation of an optimal DNA-binding sequence for the Six1 homeodomain transcription factor.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8227-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks587. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22730291 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of cranial sensory placode development.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;111:301-50. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.009. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25662264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time course and side-by-side analysis of mesodermal, pre-myogenic, myogenic and differentiated cell markers in the chicken model for skeletal muscle formation.J Anat. 2015 Sep;227(3):361-82. doi: 10.1111/joa.12353. J Anat. 2015. PMID: 26278933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudnicki M A, Schnegelsberg P N J, Stead R H, Braun T, Arnold H H, Jaenisch R. Cell. 1993;75:1351–1359. - PubMed
-
- Tajbakhsh S, Rocancourt D, Buckingham M. Nature (London) 1996;384:266–270. - PubMed
-
- Tajbakhsh S, Rocancourt D, Cossu G, Buckingham M. Cell. 1997;89:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Maroto M, Reshef R, Munsterberg A E, Koester S, Goulding M, Lassar A B. Cell. 1997;89:139–148. - PubMed
-
- Hasty P, Bradley A, Morris J H, Edmondson D G, Venuti J M, Olson E N, Klein W H. Nature (London) 1993;364:501–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

