The vesicular GABA transporter, VGAT, localizes to synaptic vesicles in sets of glycinergic as well as GABAergic neurons
- PMID: 9822734
- PMCID: PMC6793280
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09733.1998
The vesicular GABA transporter, VGAT, localizes to synaptic vesicles in sets of glycinergic as well as GABAergic neurons
Abstract
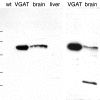
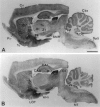
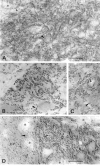
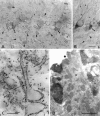
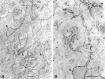
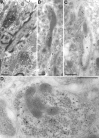
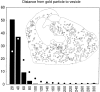
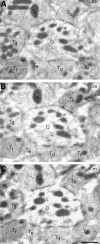
A transporter thought to mediate accumulation of GABA into synaptic vesicles has recently been cloned (McIntire et al., 1997). This vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT), the first vesicular amino acid transporter to be molecularly identified, differs in structure from previously cloned vesicular neurotransmitter transporters and defines a novel gene family. Here we use antibodies specific for N- and C-terminal epitopes of VGAT to localize the protein in the rat CNS. VGAT is highly concentrated in the nerve endings of GABAergic neurons in the brain and spinal cord but also in glycinergic nerve endings. In contrast, hippocampal mossy fiber boutons, which although glutamatergic are known to contain GABA, lack VGAT immunoreactivity. Post-embedding immunogold quantification shows that the protein specifically associates with synaptic vesicles. Triple labeling for VGAT, GABA, and glycine in the lateral oliva superior revealed a higher expression of VGAT in nerve endings rich in GABA, with or without glycine, than in others rich in glycine only. Although the great majority of nerve terminals containing GABA or glycine are immunopositive for VGAT, subpopulations of nerve endings rich in GABA or glycine appear to lack the protein. Additional vesicular transporters or alternative modes of release may therefore contribute to the inhibitory neurotransmission mediated by these two amino acids.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Vesicular gamma-aminobutyric acid transporter expression in amacrine and horizontal cells.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Apr 8;445(3):227-37. doi: 10.1002/cne.10166. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11920703 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of the vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter in GABAergic and glycinergic synaptic terminal boutons.J Cell Sci. 1999 Mar;112 ( Pt 6):811-23. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.6.811. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10036231
-
Vesicular neurotransmitter transporter expression in developing postnatal rodent retina: GABA and glycine precede glutamate.J Neurosci. 2003 Jan 15;23(2):518-29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-02-00518.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12533612 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic control of inhibitory neurotransmitter content in VIAAT containing synaptic vesicles.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27296116 Review.
-
Why glycine transporters have different stoichiometries.FEBS Lett. 2002 Oct 2;529(1):93-101. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03251-9. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12354619 Review.
Cited by
-
GABA(A) receptors implicated in REM sleep control express a benzodiazepine binding site.Brain Res. 2013 Aug 21;1527:131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.037. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23835499 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic Synapses at the Axon Initial Segment of Basolateral Amygdala Projection Neurons Modulate Fear Extinction.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Jan;42(2):473-484. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.205. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27634356 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Estrogen Receptor Beta Agonist Treatment Modifies the Hippocampal Transcriptome in Middle-Aged Ovariectomized Rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Jun 10;10:149. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00149. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27375434 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Specificity of GABAergic Regulation of Cross-Modal Plasticity in Mouse Visual Cortex after Unilateral Enucleation.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 12;35(32):11174-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3808-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26269628 Free PMC article.
-
Cracking down on inhibition: selective removal of GABAergic interneurons from hippocampal networks.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 8;32(6):1989-2001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2720-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22323713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barber R, Saito K. Light microscopic visualization of GAD and GABA-T in immunocytochemical preparations of rodent CNS. In: Roberts E, Chase TN, Tower DB, editors. GABA in nervous system function. Raven; New York: 1976. pp. 113–132.
-
- Berod A, Hartman BK, Pujol JF. Importance of fixation in immunohistochemistry: use of formaldehyde solutions at variable pH for the localization of tyrosine hydroxylase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981;29:844–850. - PubMed
-
- Blackstad TW, Karagülle T, Ottersen OP. MORFOREL, a computer program for two dimensional analysis of micrographs of biological specimens, with emphasis on immunogold preparations. Comput Biol Med. 1990;20:15–34. - PubMed
-
- Burger PM, Hell J, Mehl E, Krasel C, Lottspeich F, Jahn R. GABA and glycine in synaptic vesicles: storage and transport characteristics. Neuron. 1991;7:287–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
