The septins are required for the mitosis-specific activation of the Gin4 kinase
- PMID: 9813092
- PMCID: PMC2148151
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.3.709
The septins are required for the mitosis-specific activation of the Gin4 kinase
Abstract
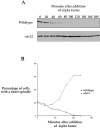
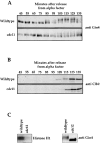
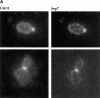
In budding yeast, a protein kinase called Gin4 is specifically activated during mitosis and functions in a pathway initiated by the Clb2 cyclin to control bud growth. We have used genetics and biochemistry to identify additional proteins that function with Gin4 in this pathway, and both of these approaches have identified members of the septin family. Loss of septin function produces a phenotype that is very similar to the phenotype caused by loss of Gin4 function, and the septins are required early in mitosis to activate Gin4 kinase activity. Furthermore, septin mutants display a prolonged mitotic delay at the short spindle stage, consistent with a role for the septins in the control of mitotic events. Members of the septin family bind directly to Gin4, demonstrating that the functions of Gin4 and the septins must be closely linked within the cell. These results demonstrate that the septins in budding yeast play an integral role in the mitosis-specific regulation of the Gin4 kinase and that they carry out functions early in mitosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Control of mitotic events by the Cdc42 GTPase, the Clb2 cyclin and a member of the PAK kinase family.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 10;8(18):991-1000. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00419-8. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9740799
-
Cell cycle-dependent assembly of a Gin4-septin complex.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jun;13(6):2091-105. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-10-0500. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12058072 Free PMC article.
-
Control of mitotic events by Nap1 and the Gin4 kinase.J Cell Biol. 1997 Jul 14;138(1):119-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.1.119. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9214386 Free PMC article.
-
The elm1 kinase functions in a mitotic signaling network in budding yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Dec;19(12):7983-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.12.7983. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10567524 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin ubiquitination: the destructive end of mitosis.Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):149-52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90322-4. Cell. 1995. PMID: 7736567 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A FRET-based method for monitoring septin polymerization and binding of septin-associated proteins.Methods Cell Biol. 2016;136:35-56. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.03.024. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Methods Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27473902 Free PMC article.
-
Central Role of the Actomyosin Ring in Coordinating Cytokinesis Steps in Budding Yeast.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;10(9):662. doi: 10.3390/jof10090662. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Essential role of the endocytic site-associated protein Ecm25 in stress-induced cell elongation.Cell Rep. 2021 May 18;35(7):109122. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109122. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34010635 Free PMC article.
-
Tor kinases are in distinct membrane-associated protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Mar;14(3):1204-20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-09-0609. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12631735 Free PMC article.
-
Shs1 plays separable roles in septin organization and cytokinesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2007 Sep;177(1):215-29. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.073007. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17603111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991;349:117–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

